LBF18109SC01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|Mass Spectra={{Image200|LBF18109SC01SP0001.gif}} (provided by Dr. Takeshi Kasama). | |Mass Spectra={{Image200|LBF18109SC01SP0001.gif}} (provided by Dr. Takeshi Kasama). | ||
|Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF18109SC01CH0001.gif}}{{Image200|LBF18109SC01CH0002.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | |Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF18109SC01CH0001.gif}}{{Image200|LBF18109SC01CH0002.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | ||
|Source=Generally considerd to be predominant fatty acid in nature (few fats known to contain less than 10%; Separation from olive oil by double fraction via urea adduct. Major constituent in plant oils e.g. olive oil (about 80%), almond oil (about 80%), mainly as glyceride. | |Source=Generally considerd to be predominant fatty acid in nature (few fats known to contain less than 10%; Separation from olive oil by double fraction via urea adduct<!--4003-->. Major constituent in plant oils e.g. olive oil (about 80%), almond oil (about 80%), mainly as glyceride. | ||
|Chemical Synthesis=Purest product (98%) obtained when the oil was saponified with 3% KOH solution; Synthesis | |Chemical Synthesis=Purest product (98%) obtained when the oil was saponified with 3% KOH solution; Synthesis<!--4008--> | ||
|Metabolism=In animals oleic acid is synthsized from stearoyl CoA by oxidative desaturation using O<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>2</FONT></SUB>, NADPH, cytochrome b<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>5</FONT></SUB>. Oleic acid is further metabolized to 20:9n-9 via reactions of desaturation and elongation. Essential fatty acid deficincy causes the accumulation of 20:9n-9. | |Metabolism=In animals oleic acid is synthsized from stearoyl CoA by oxidative desaturation using O<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>2</FONT></SUB>, NADPH, cytochrome b<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>5</FONT></SUB>. Oleic acid is further metabolized to 20:9n-9 via reactions of desaturation and elongation. Essential fatty acid deficincy causes the accumulation of 20:9n-9. | ||
|Symbol=Ole / C18:1n-9 | |Symbol=Ole / C18:1n-9 | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 26 January 2010
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0111 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030002 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF18109SC01 |
| 9-Octadecylenic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
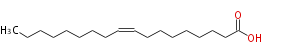
| cis-9-Octadecenoic acid | |
| |
| Ole / C18:1n-9 | |
| Formula | C18H34O2 |
| Exact Mass | 282.255880332 |
| Average Mass | 282.46136 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 12°C [labile] / 16°C [stable] | |
| 234°C at 15 mmHg | |
| dX420 0.898 | |
| 1.45823 at 20°C | |
| soluble in acetone , alcohol, chloroform, ether and petroleum ether | |
| Generally considerd to be predominant fatty acid in nature (few fats known to contain less than 10%; Separation from olive oil by double fraction via urea adduct. Major constituent in plant oils e.g. olive oil (about 80%), almond oil (about 80%), mainly as glyceride. | |
| Purest product (98%) obtained when the oil was saponified with 3% KOH solution; Synthesis | |
| In animals oleic acid is synthsized from stearoyl CoA by oxidative desaturation using O2, NADPH, cytochrome b5. Oleic acid is further metabolized to 20:9n-9 via reactions of desaturation and elongation. Essential fatty acid deficincy causes the accumulation of 20:9n-9. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | 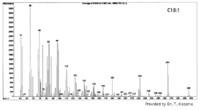 (provided by Dr. Takeshi Kasama). |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | Gas liquid chromatogram 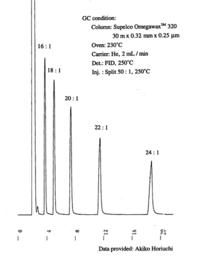 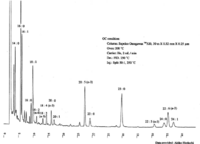 (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). |