LBF18306SC02: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|Optical=1.4800 at 20°C | |Optical=1.4800 at 20°C | ||
|Solubility=soluble in acetone, ether, methylalcohol and petroleum ether. | |Solubility=soluble in acetone, ether, methylalcohol and petroleum ether. | ||
|Source=Isolated from seeds of Oenothera biennis and O. lamarckiana (evening primroses); drying oils. A minor component of many animal lipids. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis= | |||
|Metabolism=Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is synthesized from oleic acid (18:1n-9) by desaturation of <FONT FACE="Symbol">D</FONT>12-desaturase, and <FONT FACE="Symbol">a</FONT>-linolenic acid (18:3n-3) is formed from linoleic acid by desaturation reaction of <FONT FACE="Symbol">D</FONT>15-desaturase. Since both <FONT FACE="Symbol">D</FONT>12- and 15-desaturases are present in plant cells but not in animal cells, linoleic and <FONT FACE="Symbol">a</FONT>-linolenic acid are not biosynthesized in animal cells in vivo. When ingested by animals, linoleic acid is desaturated, elongated to form <FONT FACE="Symbol">g</FONT>-linolenic acid (18:3n-6), dihomo-<FONT FACE="Symbol">g</FONT>-linolenic acid (20:3n-6), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) and adrenic acid (22:4n-6). Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-6) is synthesized from adrenic acid in significant amounts only under conditions of prolonged n-3 fatty acid deficiency., No interconversion between the n-6 and n-3 series in mammals. Nutritionally, it is important to note that different foods contain different proportions of n-6/n-3 and therefore the n-6/n-3 ratio in tissue lipids change significantly depending on the choice of foods.[[Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409}}]];> | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 22:00, 24 November 2009
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0180 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030141 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF18306SC02 |
| γ-Linolenic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
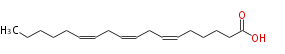
| cis-6, cis-9, cis-12-Octadecatrienoic acid | |
| |
| Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Exact Mass | 278.224580204 |
| Average Mass | 278.4296 |
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCCC(O)=O |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| -11.3 to -11°C | |
| 125°C at 0.05mmHg | |
| dX420 0.9164 | |
| 1.4800 at 20°C | |
| soluble in acetone, ether, methylalcohol and petroleum ether. | |
| Isolated from seeds of Oenothera biennis and O. lamarckiana (evening primroses); drying oils. A minor component of many animal lipids. | |
| Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is synthesized from oleic acid (18:1n-9) by desaturation of D12-desaturase, and a-linolenic acid (18:3n-3) is formed from linoleic acid by desaturation reaction of D15-desaturase. Since both D12- and 15-desaturases are present in plant cells but not in animal cells, linoleic and a-linolenic acid are not biosynthesized in animal cells in vivo. When ingested by animals, linoleic acid is desaturated, elongated to form g-linolenic acid (18:3n-6), dihomo-g-linolenic acid (20:3n-6), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) and adrenic acid (22:4n-6). Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-6) is synthesized from adrenic acid in significant amounts only under conditions of prolonged n-3 fatty acid deficiency., No interconversion between the n-6 and n-3 series in mammals. Nutritionally, it is important to note that different foods contain different proportions of n-6/n-3 and therefore the n-6/n-3 ratio in tissue lipids change significantly depending on the choice of foods. Okuyama_H et al.;> | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|