LBF20107PG03: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Miyano_M:Dorn_CR:Mueller_RA:,J. Org. Chem.,1972,37,1810|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Miyano_M:Dorn_CR:Mueller_RA:,J. Org. Chem.,1972,37,1810}}]] {{Image200|LBF20107PG03FT0001.gif}} | |Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Miyano_M:Dorn_CR:Mueller_RA:,J. Org. Chem.,1972,37,1810|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Miyano_M:Dorn_CR:Mueller_RA:,J. Org. Chem.,1972,37,1810}}]] {{Image200|LBF20107PG03FT0001.gif}} | ||
|Metabolism= | |Metabolism= | ||
|Symbol= | |Symbol=PGF1α | ||
|Biological Activity=In terms of contraction of gastrointestinal smooth muscles, prostaglandin F1 alpha was repoprted to be about 10 times less active than prostaglandin F2 alpha [[Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122}}]]. Reference [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]] contains a table for comparison of biological activities of various prostaglandins including F1 alpha . | |Biological Activity=In terms of contraction of gastrointestinal smooth muscles, prostaglandin F1 alpha was repoprted to be about 10 times less active than prostaglandin F2 alpha [[Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122}}]]. Reference [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]] contains a table for comparison of biological activities of various prostaglandins including F1 alpha . | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 03:02, 20 April 2010
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1500 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010137 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20107PG03 |
| Prostaglandin F_1α | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
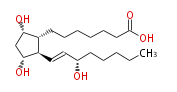
| 7- [ 3 (R) ,5 (S) -Dihydroxy-2 (R) - (3 (S) -hydroxy-1 (E) -octenyl) cyclopentan-1 (R) -yl ] -heptanoic acid | |
| |
| PGF1α | |
| Formula | C20H36O5 |
| Exact Mass | 356.256274262 |
| Average Mass | 356.49684 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](O)C=C[C@H]([C@H]1CCCCCCC(O)=O)[C@@H](C[C@@H]1O)O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 102-103°C | |
| [ α ]X25 D =+30°(ETHANOL) Pike_JEet al. | |
| DIETHYL ETHER, ETHYL ACETATE, METHANOL , ETHANOL Pike_JEet al. | |
| Prostaglandin F1 alpha is contained in human seminal plasma in an amount of 3.6 microgram/ml Bergstrom_S , and is detected in ovine seminal plasma and seminal vesicle, human amniotic fluid, umbilical cord, placental vessels and decidua, frog spinal cord and intestine, and rat adrenal Horton_EW . | |
Miyano_M et al.  | |
| In terms of contraction of gastrointestinal smooth muscles, prostaglandin F1 alpha was repoprted to be about 10 times less active than prostaglandin F2 alpha Horton_EW . Reference Bergstrom_S et al. contains a table for comparison of biological activities of various prostaglandins including F1 alpha . | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | m/e 356(M+), 338, 320 Ramwell_PW et al. |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | d,l-PGF1 α ; KBr : ν 3330, 1716, 967 cm-1 MiyanoMet al. |
| NMR Spectra | 1H-NMR(ACETONE-d6, TMS) : δ 5.50(2H, 13-,14-CH), 3.75-4.3(m, 3H), 0.88(t, 3H) Ramwell_PW et al.1H-NMR(CD3OD, TMS, 300MHz): δ 4.10(1H, 9-CH), 3.81(1H, 11-CH), 2.36(1H, 10 β -CH), 1.57(1H, 10 α -CH) De_ClercqPet al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|