LBF20207PG22: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|IR Spectra=KBr : 3400-2500, 1740, 1700, 975cm<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>-</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP> [[Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115}}]] | |IR Spectra=KBr : 3400-2500, 1740, 1700, 975cm<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>-</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP> [[Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115}}]] | ||
|NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP>H-NMR(270MHz, CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT> 5.63(dd,J=7 & 16Hz,1H,14-CH), 5.43(dd,J=16 & 8.5Hz,1H,13-CH), 4.47(m, 1H, 9-CH), 4.09(bq, J=7Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 2.87(dd, J=12 & 8.5Hz, 1H, 12-CH), 2.45(m, 2H, 10-CH2), 1.95(bm, 1H, 8-CH) [[Reference:Jenny_EF:Schaeublin_P:,Tetrah. Lett.,1974,,2235|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Jenny_EF:Schaeublin_P:,Tetrah. Lett.,1974,,2235}}]] | |NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP>H-NMR(270MHz, CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT> 5.63(dd,J=7 & 16Hz,1H,14-CH), 5.43(dd,J=16 & 8.5Hz,1H,13-CH), 4.47(m, 1H, 9-CH), 4.09(bq, J=7Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 2.87(dd, J=12 & 8.5Hz, 1H, 12-CH), 2.45(m, 2H, 10-CH2), 1.95(bm, 1H, 8-CH) [[Reference:Jenny_EF:Schaeublin_P:,Tetrah. Lett.,1974,,2235|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Jenny_EF:Schaeublin_P:,Tetrah. Lett.,1974,,2235}}]] | ||
|Source=In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin D2. Prostaglandin D2 is produced in barin, lung, spleen, mast cells and other tissues [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]] | |Source=In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin D2. Prostaglandin D2 is produced in barin, lung, spleen, mast cells and other tissues [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]]. | ||
|Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115}}]] | |Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Tanouchi_T:,J. Org. Chem.,1973,38,2115}}]] {{Image200|LBF20207PG22FT0001.gif}} | ||
|Metabolism=Prostaglandin D2 is produced by isomerization of 9,11-endoperoxide of prostaglandin H2. There are two isozymes of prostaglandin D synthase (hematopoietic type and lipocalin type) distinguished by glutathione reequirement and effect of inhibitor [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]] | |Metabolism=Prostaglandin D2 is produced by isomerization of 9,11-endoperoxide of prostaglandin H2. There are two isozymes of prostaglandin D synthase (hematopoietic type and lipocalin type) distinguished by glutathione reequirement and effect of inhibitor [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]]. Prostaglandin D2 is either reduced to 9<FONT FACE="Symbol">a</FONT>,11<FONT FACE="Symbol">b</FONT>-prostaglandin F or oxidized to 15-keto-prostaglandin D2 by a specific dehydrogenase [[Reference:Giles_H:Leff_P:,Prostaglandins,1988,35,277|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Giles_H:Leff_P:,Prostaglandins,1988,35,277}}]]. Non-enzymatic transformation of prostaglandin D2 produces anti-neoplastic <FONT FACE="Symbol">D</FONT>12-prostaglandin J2 [[Reference:Negishi_M:Koizumi_T:Ichikawa_A:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,443|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Negishi_M:Koizumi_T:Ichikawa_A:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,443}}]]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 25 November 2009
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1301 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010004 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20207PG22 |
| PROSTAGLANDIN D2 | |
|---|---|
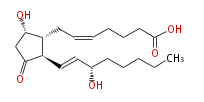
| |
| Structural Information | |
| 7- [ 5 (S) -Hydroxy-2 (R) - (3 (S) -hydroxy-1 (E) -octenyl) -3-oxocyclopentan-1 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid | |
| |
| Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Exact Mass | 352.224974134 |
| Average Mass | 352.46508 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](O)C=C[C@H]([C@H]1CC=CCCCC(O)=O)C(C[C@@H]1O)=O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 68°C Hayashi_M et al. | |
| ETHYL ACETATE,THF,CHLOROFORM OgawaYet al. | |
| In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin D2. Prostaglandin D2 is produced in barin, lung, spleen, mast cells and other tissues Urade_Y et al.. | |
|
Hayashi_M et al. | |
| Prostaglandin D2 is produced by isomerization of 9,11-endoperoxide of prostaglandin H2. There are two isozymes of prostaglandin D synthase (hematopoietic type and lipocalin type) distinguished by glutathione reequirement and effect of inhibitor Urade_Y et al.. Prostaglandin D2 is either reduced to 9a,11b-prostaglandin F or oxidized to 15-keto-prostaglandin D2 by a specific dehydrogenase Giles_H et al.. Non-enzymatic transformation of prostaglandin D2 produces anti-neoplastic D12-prostaglandin J2 Negishi_M et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | m/e 334, 316, 246, 245, 191, 190, 161, 55 OgawaYet al. |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | KBr : 3400-2500, 1740, 1700, 975cm-1 HayashiMet al. |
| NMR Spectra | 1H-NMR(270MHz, CDCl3) : d 5.63(dd,J=7 & 16Hz,1H,14-CH), 5.43(dd,J=16 & 8.5Hz,1H,13-CH), 4.47(m, 1H, 9-CH), 4.09(bq, J=7Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 2.87(dd, J=12 & 8.5Hz, 1H, 12-CH), 2.45(m, 2H, 10-CH2), 1.95(bm, 1H, 8-CH) Jenny_EF et al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|