LBF20207PG23: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|IR Spectra=d,l-mixture ; 3400, 1710, 970cm<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>-</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP> [[Reference:Chen_SML:Schaub_RE:Grudzinskas_CV:,J. Org. Chem.,1978,43,3450|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Chen_SML:Schaub_RE:Grudzinskas_CV:,J. Org. Chem.,1978,43,3450}}]] | |IR Spectra=d,l-mixture ; 3400, 1710, 970cm<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>-</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP> [[Reference:Chen_SML:Schaub_RE:Grudzinskas_CV:,J. Org. Chem.,1978,43,3450|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Chen_SML:Schaub_RE:Grudzinskas_CV:,J. Org. Chem.,1978,43,3450}}]] | ||
|NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUP>C-NMR(CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : 214.71(C9),178.39(C1), 136.62(C14), 131.52(C13), 130.91(C5), 126.69(C6), 73.19(C15), 72.13(C11), 54.55(C12), 53.51(C8), 46.23(C10), 37.00 (C16), 33.56(C2), 31.73(C18), 26.47(C4), 25.20(C7,17), 24.60(C3), 22.64(C19), 14.04. [[Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167}}]]. <SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP>H-NMR(CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT>5.67(dd, J=6.6Hz, 15.4, 1H, 14-CH), 5.57(dd, J=8.1, 15.4Hz, 1H, 13-CH), 5.40(m, 2H, 5.6-CH), 4.12(q, J=6.5, 6.7, 6.8Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 4.06(q, J=8.1, 8.2, 8.3Hz, 1H, 11-CH), 2.72(dd, J= [[Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167}}]] | |NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUP>C-NMR(CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : 214.71(C9),178.39(C1), 136.62(C14), 131.52(C13), 130.91(C5), 126.69(C6), 73.19(C15), 72.13(C11), 54.55(C12), 53.51(C8), 46.23(C10), 37.00 (C16), 33.56(C2), 31.73(C18), 26.47(C4), 25.20(C7,17), 24.60(C3), 22.64(C19), 14.04. [[Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167}}]]. <SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP>H-NMR(CDCl<SUB><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUB>) : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT>5.67(dd, J=6.6Hz, 15.4, 1H, 14-CH), 5.57(dd, J=8.1, 15.4Hz, 1H, 13-CH), 5.40(m, 2H, 5.6-CH), 4.12(q, J=6.5, 6.7, 6.8Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 4.06(q, J=8.1, 8.2, 8.3Hz, 1H, 11-CH), 2.72(dd, J= [[Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Donaldson_RE:Saddler_JC:Byrn_S:McKenzie_AT:Fuchs_PL:,J. Org. Chem.,1983,48,2167}}]] | ||
|Source=Prostaglandin E2 was found to be accummulating in human semen in an amount of about 13 microgram per ml [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382}}]];>. In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin E2. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis={{Image200|XPR1401FT0001.gif}} [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397}}]];> | |||
|Metabolism=Prostaglandin E2 is produced from arachidonic acid via prostaglandins G2 and H2 by the catalyses of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) [[Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157}}]];> and prostaglandin E synthase [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]];>. Two isoforms of the cyclooxygnease enzyme responsible for prostaglandin H2 synthesis are present. Cyclooxygenase-1 is constitutively found in most mammalian tissues, while cyclooxygnease-2 is induced rapidly and transiently in physiological and pathological events, especially in inflammation [[Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157}}]];>. The biological activities of prostaglandin E2 are lost by oxidation of its 15-hydroxyl group catalyzed by 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [[Reference:Hansen_HS:,Prostaglandins,1976,12,647|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hansen_HS:,Prostaglandins,1976,12,647}}]];>. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 22:00, 24 November 2009
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1401 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010003 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20207PG23 |
| Prostaglandin E2 | |
|---|---|
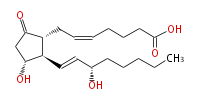
| |
| Structural Information | |
| 7- [ 3 (R) -Hydroxy-2 (R) - (3 (S) -hydroxy-1 (E) -octenyl-5-oxocyclopentan-1 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid | |
| |
| Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Exact Mass | 352.224974134 |
| Average Mass | 352.46508 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](O)C=C[C@H]([C@H]1CC=CCCCC(O)=O)[C@@H](CC1=O)O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 65-66°C Corey_EJ et al. | |
| ETHYL ACETATE,THF,CHLOROFORM Donaldson_RE et al. Sih_CJ et al.. STABILITIES: to be stable under neutral condition. to decompose to PGA2 under acidic and to PGB2 under basic conditions Karim_SM et al. Pike_JEet al. | |
| Prostaglandin E2 was found to be accummulating in human semen in an amount of about 13 microgram per ml Bergstrom_S ;>. In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin E2. | |
File:XPR1401FT0001.gif Corey_EJ et al.;> | |
| Prostaglandin E2 is produced from arachidonic acid via prostaglandins G2 and H2 by the catalyses of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) Smith_WL et al.;> and prostaglandin E synthase Urade_Y et al.;>. Two isoforms of the cyclooxygnease enzyme responsible for prostaglandin H2 synthesis are present. Cyclooxygenase-1 is constitutively found in most mammalian tissues, while cyclooxygnease-2 is induced rapidly and transiently in physiological and pathological events, especially in inflammation Smith_WL et al.;>. The biological activities of prostaglandin E2 are lost by oxidation of its 15-hydroxyl group catalyzed by 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase Hansen_HS ;>. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | d,l-mixture ; 334(M+-18), 316, 298, 190 Chen_SML et al. |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | d,l-mixture ; 3400, 1710, 970cm-1 Chen_SML et al. |
| NMR Spectra | 13C-NMR(CDCl3) : 214.71(C9),178.39(C1), 136.62(C14), 131.52(C13), 130.91(C5), 126.69(C6), 73.19(C15), 72.13(C11), 54.55(C12), 53.51(C8), 46.23(C10), 37.00 (C16), 33.56(C2), 31.73(C18), 26.47(C4), 25.20(C7,17), 24.60(C3), 22.64(C19), 14.04. Donaldson_RE et al.. 1H-NMR(CDCl3) : d5.67(dd, J=6.6Hz, 15.4, 1H, 14-CH), 5.57(dd, J=8.1, 15.4Hz, 1H, 13-CH), 5.40(m, 2H, 5.6-CH), 4.12(q, J=6.5, 6.7, 6.8Hz, 1H, 15-CH), 4.06(q, J=8.1, 8.2, 8.3Hz, 1H, 11-CH), 2.72(dd, J= Donaldson_RE et al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|