LBF20207PG27: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|Common Name=&&PROSTAGLANDIN G_2&&7- [ 2 (R) - (3 (S) -Hydroperoxy-1 (E) -octenyl) -1 (R) ,4 (S) -5,6-dioxabicyclo [ 2.2.1 ] -heptan-3 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid&& | |Common Name=&&PROSTAGLANDIN G_2&&7- [ 2 (R) - (3 (S) -Hydroperoxy-1 (E) -octenyl) -1 (R) ,4 (S) -5,6-dioxabicyclo [ 2.2.1 ] -heptan-3 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid&& | ||
|NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUP>C-NMR : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT> 84.6(C15) [[Reference:Porter_NA:Byers_JD:Ali_AE:Eling_TE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1980,102,1183|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Porter_NA:Byers_JD:Ali_AE:Eling_TE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1980,102,1183}}]] | |NMR Spectra=<SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>1</FONT></SUP><SUP><FONT SIZE=-1>3</FONT></SUP>C-NMR : <FONT FACE="Symbol">d</FONT> 84.6(C15) [[Reference:Porter_NA:Byers_JD:Ali_AE:Eling_TE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1980,102,1183|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Porter_NA:Byers_JD:Ali_AE:Eling_TE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1980,102,1183}}]] | ||
|Source=Prostaglandin G2 is produced by bis-dioxygenation and cyclization of arachidonic acid as an intermediate for the biosyntheses of various prostaglandins and thromboxanes. The responsible enzyme is prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase usually referred to as fatty acid cyclooxygenase, and distributed in various animal tissues ;>. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis= {{Image200|XPR1601FT0001.gif}} | |||
|Metabolism=Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase is a bifunctional enzyme with an oxygenase activity (fatty acid cyclooxygenase) producing prostaglandin G2 from arachidonic acid and a peroxidase activity (prostagladnin hydroperoxidase) converting prostaglandin G2 to prostaglandin H2 . The enzyme is usually referred to briefly as cyclooxygenase. There are two isozymes of the enzyme. Cyclooxygenase-1 is a constitutive enzyme expressed in most mammalian cells, while cyclooxygenase-2 is a product of immediate early gene and is induced rapidly and transiently in certain types of cell by various bioactive compounds [[Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Smith_WL:Garavito_RM:DeWitt_DL:,J. Biol. Chem.,1996,271,33157}}]][[Reference:Funk_CD:,Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.,1993,45,67|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Funk_CD:,Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.,1993,45,67}}]];>. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 22:00, 24 November 2009
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1601 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010009 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20207PG27 |
| PROSTAGLANDIN G2 | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
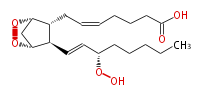
| 7- [ 2 (R) - (3 (S) -Hydroperoxy-1 (E) -octenyl) -1 (R) ,4 (S) -5,6-dioxabicyclo [ 2.2.1 ] -heptan-3 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid | |
| |
| Formula | C20H32O6 |
| Exact Mass | 368.219888756 |
| Average Mass | 368.46448 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](OO)C=C[C@@H]([C@H]21)[C@@H](CC=CCCCC(O)=O)[C@@H](OO2)C1)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| Prostaglandin G2 is produced by bis-dioxygenation and cyclization of arachidonic acid as an intermediate for the biosyntheses of various prostaglandins and thromboxanes. The responsible enzyme is prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase usually referred to as fatty acid cyclooxygenase, and distributed in various animal tissues ;>. | |
File:XPR1601FT0001.gif | |
| Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase is a bifunctional enzyme with an oxygenase activity (fatty acid cyclooxygenase) producing prostaglandin G2 from arachidonic acid and a peroxidase activity (prostagladnin hydroperoxidase) converting prostaglandin G2 to prostaglandin H2 . The enzyme is usually referred to briefly as cyclooxygenase. There are two isozymes of the enzyme. Cyclooxygenase-1 is a constitutive enzyme expressed in most mammalian cells, while cyclooxygenase-2 is a product of immediate early gene and is induced rapidly and transiently in certain types of cell by various bioactive compounds Smith_WL et al. Funk_CD ;>. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | 13C-NMR : d 84.6(C15) Porter_NA et al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|