Category:LBGPC: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Lipid/Header}} | |||
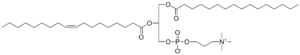
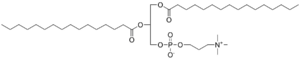
=Phosphatidyl Choline= | =Phosphatidyl Choline= | ||
{{twocolumn| | {{twocolumn| | ||
The phosphatidyl cholines, or PCs, are abundant phospholipids in animal and plant cells. | The phosphatidyl cholines, or PCs, are abundant phospholipids in animal and plant cells. They are also called lecithin, especially in nutritional study. | ||
| | | | ||
ホスファチジルコリン(PC)は動物・植物の細胞における主要なリン脂質です。栄養学の分野ではレシチンとも呼ばれます。 | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
==Essentiality== | ==Essentiality== | ||
{{twocolumn| | {{twocolumn| | ||
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' completely lack PCs, and its functions are complemented with diacylglyceryltrimethyl-homoserine (DGTS).<ref>Vogel G, Eichenberger W (1992) Betaine lipids in lower plants. Biosynthesis of DGTS and DGTA in Ochromonas danica (Chrysophyceae) and the possible role of DGTS in lipid metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol. 33:427 [http://pcp.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/4/427.abstract pdf]</ref><ref>Moore TS, Du Z, Chen Z (2001) Membrane lipid biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In vitro biosynthesis of diacylglyceryltrimethylhomoserine. Plant Physiol. 125(1):423 PMID 11154349</ref> Other chlamydomonas species contain both PCs and DGTSs. | ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' completely lack PCs, and its functions are complemented with diacylglyceryltrimethyl-homoserine (DGTS) and PEs.<ref>Vogel G, Eichenberger W (1992) Betaine lipids in lower plants. Biosynthesis of DGTS and DGTA in Ochromonas danica (Chrysophyceae) and the possible role of DGTS in lipid metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol. 33:427 [http://pcp.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/4/427.abstract pdf]</ref><ref>Moore TS, Du Z, Chen Z (2001) Membrane lipid biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In vitro biosynthesis of diacylglyceryltrimethylhomoserine. Plant Physiol. 125(1):423 PMID 11154349</ref> Other chlamydomonas species contain both PCs and DGTSs. | ||
|''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' はPCを全く持たず、その機能はジアシルグリセリルトリメチルホモセリン (DGTS) | <p>Many archaea also lack PCs. | ||
|''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' はPCを全く持たず、その機能はジアシルグリセリルトリメチルホモセリン (DGTS) やPEで代替されています。他のクラミドモナスは PC も DGTS も持っています。 | |||
多くのアーキアには、PCがありません。 | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:18, 20 July 2016
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
Phosphatidyl Choline
The phosphatidyl cholines, or PCs, are abundant phospholipids in animal and plant cells. They are also called lecithin, especially in nutritional study. |
ホスファチジルコリン(PC)は動物・植物の細胞における主要なリン脂質です。栄養学の分野ではレシチンとも呼ばれます。 |
- Major composition
- Ether-type PC
The sn-1 position of PC can be ether form instead of the standard acyl form. The 1-alkylated chain has 16 or 18 carbons and present in all kinds of cells. A particular 1-alkyl-2-acetyl PC is called platelet activating factor (PAF) [1], and it also is a inflammation mediator. Synthetic alkyl lipids, such as edelfosine (1-O-octadecyl-2-O-methyl-PC), function as antitumor agents. |
PCの sn-1 はエーテル結合の場合もあり、鎖長16または18のものがほぼ全ての細胞に見つかります。特に 1-アルキル-2アセチルのPCは血小板活性化因子 (PAF) と呼ばれ、炎症をひきおこします。edelfosineのように両方がアルキルの合成PCは抗腫瘍効果を示します。 |
- Alkenyl-type PC
The 1-alk-1′-enyl-2-acyl-PCs are called alkenylphosphatidylcholines (or plasmenylcholines). Together with plasmenyl ethanolamine forms, they are called plasmalogens and mainly localize in peroxysomes. |
1-alkylでエーテル結合の隣に二重結合のあるPCは、アルケニルホスファチジルコリンまたはプラスメニルコリンと呼ばれます。プラスメニルエタノールアミンとあわせてプラズマローゲンと呼ばれ、多くがペロキシソームに局在します。 |
Function
- Signaling agent
The hydrolysis of PC by phospholipases C and D in response to agonists such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) produces phosphatidic acid and phosphocholine. |
血小板由来増殖因子などのアゴニストに対し、PCがホスホリパーゼCまたはDにより加水分解されると、二次メッセンジャーであるホスファチジン酸を産生します。 |
- Phagocytosis
The 2-lyso-derivatives by the phospholipase A2 activity stimulate phagocyte recruitment and phagocytosis. They also cause demyelination of dendrites. |
ホスホリパーゼA2により産生する2-リゾ体は、食細胞を刺激し貪食作用をおこします。また神経細胞を脱ミエリン化させます。 |
- LDL recognition
sn-2 oxidized forms of PC16:0-18:1 and PC16:0-22:4 function as the ligands for CD36 receptor. Macrophages use them to identify oxidized forms of low density lipoprotein (LDL).[2] |
PC16:0-18:1 や PC16:0-22:4 の sn-2 が酸化してアルデヒドやアルコールになったものがCD36受容体のリガンドになります。マクロファージがこれらの分子を認識して酸化LDLを見分けます。 |
Essentiality
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii completely lack PCs, and its functions are complemented with diacylglyceryltrimethyl-homoserine (DGTS) and PEs.[3][4] Other chlamydomonas species contain both PCs and DGTSs. Many archaea also lack PCs. |
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii はPCを全く持たず、その機能はジアシルグリセリルトリメチルホモセリン (DGTS) やPEで代替されています。他のクラミドモナスは PC も DGTS も持っています。 多くのアーキアには、PCがありません。 |
- References
- ↑ Demopoulos CA, Pinckard RN, Hanahan DJ (1979) "Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators)" J Biol Chem 254(19):9355 PMID 489536
- ↑ Podrez EA, Poliakov E, et al. (2002) "Identification of a novel family of oxidized phospholipids that serve as ligands for the macrophage scavenger receptor CD36" J Biol Chem 277(41):38503. PMID 12105195
- ↑ Vogel G, Eichenberger W (1992) Betaine lipids in lower plants. Biosynthesis of DGTS and DGTA in Ochromonas danica (Chrysophyceae) and the possible role of DGTS in lipid metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol. 33:427 pdf
- ↑ Moore TS, Du Z, Chen Z (2001) Membrane lipid biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In vitro biosynthesis of diacylglyceryltrimethylhomoserine. Plant Physiol. 125(1):423 PMID 11154349
This category currently contains no pages or media.