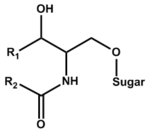
(weight %) From: Yamakawa T, Nishimura S. "Cerebroside composition in animal brain" Jpn J Exp 1966;36:101 PMID 5297247
Fatty acid composition of bovine brains
| Nonhydroxy fatty acid (adjusted GC peak %)
|
Hydroxy fatty acid
|
| fatty acid |
Ceramide |
Sphingomyelin |
Cerebroside |
Sulfatide |
fatty acid |
Cerebroside |
Sulfatide
|
| 12:0
|
- |
12h:0 |
0.4 |
0.3
|
| 13:0
|
- |
13h:0 |
0.2 |
0.2
|
| 14:0 |
0.6 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.8 |
14h:0 |
0.8 |
3.9
|
| 15:0 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
tr. |
0.3 |
15h:0 |
tr. |
0.3
|
| 16:0 |
4.5 |
5.9 |
3.5 |
4.1 |
16h:0 |
0.1 |
0.7
|
| 16:1 |
0.4 |
tr. |
0.1 |
0.7 |
16h:1 |
tr. |
1.7
|
| 17:0 |
tr. |
0.3 |
tr. |
tr. |
17h:0 |
0.2 |
0.9
|
| 18:0 |
35.2 |
40.1 |
5.8 |
3.3 |
18h:0 |
16.2 |
12.3
|
| 18:1 |
2.1 |
0.7 |
2.7 |
5.2 |
18h:1 |
- |
-
|
| 19:0 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
19h:0 |
0.4 |
0.3
|
| 20:0 |
1.0 |
0.4 |
0.6 |
0.3 |
20h:0 |
0.5 |
0.7
|
| 20:1 |
0.5 |
tr. |
0.3 |
0.4 |
20h:1 |
- |
-
|
| 21:0 |
tr. |
tr. |
- |
- |
21h:1 |
- |
-
|
| 22:0 |
3.3 |
3.5 |
3.6 |
3.5 |
22h:0 |
5.8 |
7.7
|
| 22:1 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
22h:1 |
- |
-
|
| 23:0 |
3.7 |
2.8 |
5.2 |
3.1 |
23h:0 |
8.9 |
6.5
|
| 23:1 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.2 |
0.8 |
23h:1 |
- |
-
|
| 24:0 |
9.8 |
10.7 |
17.4 |
17.8 |
24h:0 |
30.1 |
26.0
|
| 24:1 |
18.4 |
24.6 |
39.3 |
39.5 |
24h:1 |
14.6 |
16.7
|
| 25:0 |
1.4 |
1.5 |
3.6 |
2.2 |
25h:0 |
7.0 |
4.5
|
| 25:1 |
3.0 |
3.3 |
6.2 |
5.2 |
25h:1 |
3.0 |
2.8
|
| 26:0 |
2.3 |
0.6 |
1.7 |
2.3 |
26h:0 |
3.9 |
3.8
|
| 26:1 |
3.6 |
2.6 |
7.6 |
8.5 |
26h:1 |
6.3 |
6.5
|
| 27:0 |
2.9 |
- |
- |
- |
27h:0 |
- |
-
|
| 27:1 |
1.8 |
- |
tr. |
- |
27h:1 |
- |
-
|
| From: O'Brien JS, Rouser G "The fatty acid composition of brain sphingolipids: sphingomyelin, ceramide, cerebroside, and cerebroside sulfate"J Lipid Res1964; 5:339-342.PMID 5873370 Per cent of FA of each column. No PUFA, trace amount of hydroxy FA in ceramide, no hydroxy FA in sphingomyelin. The total ratio of nonhydroxy to hydroxy acids in cerebroside and sulfatide were 42:58 and 77:23, respectively (77:13 in the original paper). Human brain has a similar composition.
|
Cerebrosides in All Kingdoms
The table lists biological species from which sphingolipids were identified. Icons indicate representative species. The icons are used in sphingolipid references together with  for chemical synthesis. for chemical synthesis.
|
ここに示す分類表にはスフィンゴ脂質が報告された生物が記載されており、アイコンは代表種を表します。スフィンゴ脂質関連の文献にはこれらのアイコンの他、化学合成を表す も使われます。 も使われます。
|
| Domain
|
Kingdom
|
Phylum
|
Class
|
Order
|
Model organism
|
Icon
|
Galactosylceramides (GalCer)
(*β configuration unless otherwise state)
|
Glucosylceramides (GlcCer)
(*β configuration unless otherwise state)
|
Glycosphingolipids
(GSL)
|
Ceramide phosphoethanolamine
(CPE)
|
Sphingomyelin
(SM)
|
Ceramide aminoethylphosphonate
(CAEP)
|
Ceramide methylaminoethylphosphonate
(CMAEP)
|
Glycosyl inositol phosphoceramides
(GIPC)
|
| ドメイン
|
界
|
門
|
綱
|
目
|
モデル生物
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Major series
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
Species
(Structure)
|
FA, LCB
|
References
|
真正細菌
Bacteria
|
|
バクテロイデス門
Bacteroidetes
|
|
|
腸内細菌
|
|
Bacteroides
fragilis
(α-GalCer)
|
br-h17:0,
br-d17:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bacteroides
fragilis
|
br-h17:0,
br-d17:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sphingobacterium
spiritivorum
/ATCC33861
(Ins-P-Cer)
|
br-15:0,
br-h15:0,
br-d17:0
|
PubMed
|
シアノバクテリア門
Cyanobacteria
|
|
|
藍色細菌
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scytonema
julianum
(Acetyl-
sphingomyelin)
|
15:1,d18:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
プロテオバクテリア門
Proteobacteria
|
|
|
大腸菌
|
Cystobacter
fuscus
(β-GalCer)
|
br-h17:0,
br-d19:2
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
Sphingomonas
paucimobilis
(GlcAα-Cer)
|
h14:0,d18:0
|
PubMed
|
|
Sorangium
cellulosum
|
h16:1,
br-h17:1,
h18:1,
br-d21:3,
br-d21:2
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
Bacteriovorax
stolpii
|
br-h15:0,
br-15:0,
br-t17:0,
br-d17:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
真核生物
Eukaryota
|
原生生物界
Protista
|
メタモナーダ門 Metamonada
|
|
|
鞭毛虫
|

|
|
|
|
Giardia
lamblia
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
Trichomonas
vaginalis
|
16:0,d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Giardia
lamblia
|
16:0,d18:1
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ユーグレノゾア門
Euglenozoa
|
|
|
|
|
|
Leishmania
amazonensis
Plasmodium
falciparum
|
undescribed
h10:0,h120,
d18:0,d20:0
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
Leishmania
amazonensis
(Galβ1-3Galα1
-4Galβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Plasmodium
falciparum
(trihexosyl-
ceramide)
Trypanosoma
brucei
(GM3,GM1,
GD1a,GD1b)
|
undescribed
h12:0,h14:0,
d18:0,d20:0
undescribed
|
PubMed
PubMed
PubMed
|
Globo,
a-series,
b-series
|
Leishmania
major
|
18:0,d16:1
|
PubMed
|
Plasmodium
falciparum
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trypanosoma
brucei
(Ins-P-Cer)
|
16:0,17:0,
18:0 d16:0,
d17:0,d18:1,
d18:0,d19:0,
d20:0,d20:1
|
PubMed
(*Procyclic
formのみ)
|
繊毛虫門
Ciliophora
|
|
|
繊毛虫
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entodinium
caudatum
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
Tetrahymena
pyriformis
/WH-14
|
16:0,
br-17:0,
br-18:0,
br-h17:0,
h18:0,
br-d17:1,
br-d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Tetrahymena
pyriformis
/WH-14
|
16:0,
br-18:0,
br-h17:0,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
植物界
Plantae
|
緑藻植物門
Chlorophyta
|
|
|
クロレラ
|

|
|
|
|
Pseudococcomyxa
chodatii
|
h16:0,h18:0,h20:0,
h22:0,h24:0
d18:2,t18:0,t18:1
|
DOI
|
Chlorella
kessleri
(Galα1-4Galβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Globo
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorella
variabilis
(Hex(2)-Ins
-P-Cer)
|
h24:1, t18:0
|
Nebraska
Univ.,2015
(*学位論文。
ESI-MS分析,
糖の種類は
Hexとしか
判別できない)
|
ストレプト植物門
Streptophyta
(*被子植物門を除く) (except Angiosperm)
|
|
|
緑色植物
|
|
|
|
Ginkgo
biloba
Stenochlaena
palustris
|
h16:0,d18:2
h24:0,d18:2
|
DOI
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pteridum
aquilinum
(HexNAc-HexA
-(Hex-)Ins
-P-Cer)
|
h24:0,t18:0
|
PubMed
(*MALDI-MS分析,
糖の種類は
Hexとしか
判別できない)
|
被子植物門
Angiosperm
|
|
|
シロイヌナズナ
|
|
|
|
Arabidopsis
thaliana
|
16:0,h24:1,
d18:1,t18:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prunus
armeniaca
/kernel
|
undescribed
|
J.Chromatogra.,
294,519-524,
1984
|
|
|
|
Arabidopsis
thaliana
/leaves
(Glc-GlcA
-Ins-P-Cer)
|
h24:0,t18:1
|
PubMed
|
菌界
Fungi
|
接合菌門
Zygomycota
|
|
|
ケカビ、クモノスカビ
|

|
|
|
|
Mucor
hiemalis
|
h14:0,h16:0,
br-d19:2,d20:1
|
PubMed
|
Mucor
hiemalis
(Galβ1-6Galβ1
-Cer)
|
h24:0,h25:0,
h26:0,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Gala
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PubMed
(*接合菌門に
はGIPC
は含まれ
ない。)
|
子嚢菌門
Ascomycota
|
|
|
酵母、コウジカビ
|
Aspergillus
oryzae
|
h18:0,br-d19:2
|
PubMed
|
Aspergillus
oryzae
|
h18:0,br-d19:2
|
PubMed
|
Neurospora
crassa
(Glcα1-2Galβ1-
6Galβ1-6Galβ1-Cer)
|
h24:0,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Gala
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aspergillus
nidulans
(Manα1-3Manα
-2Ins-P-Cer)
|
h24:0,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
担子菌門
Basidiomycota
|
|
|
キノコ
|
|
|
|
Cryptococcus
neoformans
|
h18:0,br-d19:2
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cryptococcus
neoformans
(Ins-P-6Manα1
-2Ins-P-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
動物界
Animalia
|
海綿動物門
Porifera
|
|
|
カイメン
|

|
Agelas
mauritianus
(α-GalCer)
Chondropsis sp.
(β-GalCer)
|
h24:0,br-t18:0
h24:0,br-d18:1
|
DOI
DOI
|
Haliclona sp.
|
h22:0,t18:1
|
DOI
|
Amphimedon
viridis
(GlcNAcα1-Cer,
GlcNAcβ1-Cer)
|
h22:0,br-t20:1,
h22:0,br-t20:1,
br-t19:0
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Svenzea
zeai
(Arapβ1
-6Ins-P-Cer)
|
16:0,
br-16:0,
br-17:0,
d26:1,d26:0
|
PubMed
|
刺胞動物門
Cnidaria
|
|
|
クラゲ
|

|
|
|
|
Metridium
senile
Sarcophyton ehrenbergi
(α-GlcCer)
|
h16:0,h20:0,
br-d19:2
h18:0,br-d19:3
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PubMed
(*刺胞動物門はCPEをもたない。)
|
|
|
PubMed
(*刺胞動物門はSMをもたない。)
|
Aurelia
aurita
|
14:0,16:0,
d18:1,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Aurelia
aurita
|
14:0,16:0,
d18:1,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
(旧口動物、冠輪)
(Protostomia, Lophotrochozoa)
|
扁形動物門
Platyhelminthes
|
吸虫綱
Trematoda
|
|
ジストマ
|

|
Fasciola
hepatica
|
18:0,h18:0,
t18:0,t20:0
|
PubMed
|
Fasciola
hepatica
Schistosoma mansoni
|
18:0,h18:0,
t18:0,t20:0
h16:0,t18:0,
t20:0
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
Fasciola
hepatica
(Galα1-4Galβ1
-4-Glcβ1-Cer)
Schistosoma
mansoni
(GalNAcβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Schistosoma
mansoni
(GM1,GD1a,
GD1b,GT1b)
|
undescribed
h16:0,26:0
undescribed
|
PubMed
PubMed
DOI
|
Globo,
Schisto,
Ganglio,
a-series
|
|
|
|
Paramphistomum
cervi
|
16:0,18:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
渦虫綱
Tubellaria
|
|
プラナリア
|
|
|
|
Dugesia
dorotocephala
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
条虫綱
Cestoda
|
|
サナダムシ
|
Diphyllobothrium
hottai
|
16:0,18:0,26:0,
28:0,d18:0,
d20:0,t18:0,
t20:0
|
PubMed
|
Diphyllobothrium
hottai
|
16:0,18:0,
26:0,28:0,
d18:0,d20:0,
t18:0,t20:0
|
PubMed
|
Diphyllobothrium
hottai
(Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glcβ1-3Galβ1-Cer)
Spirometra
erinacei
(Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glcβ1-3Galβ1-Cer)
Echinococcus
multilocularis
(GM1,GM3,
GD1a,GM2)
|
16:0,18:0,
26:0,28:0,
d18:0,d20:0,
t18:0
18:0,18:1,
d18:0,t18:0
16:0,24:0,
24:1,d18:1
|
PubMed
PubMed
PubMed
|
Spirometo,
a-series
|
|
|
|
Hymenolepis
diminuta
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
外肛動物門
Bryozoa
|
|
|
コケムシ
|
|
|
|
|
Pectinatella
magnifica
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
Pectinatella
magnifica
(GlcNAcβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
腕足動物門
Brachiopoda
|
|
|
シャミセンガイ
|

|
|
|
|
Lingula
unguis
|
h16:0,h17:0,
h18:0,d18:1,
d18:3
|
DOI
|
Lingula
unguis
(Manα1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,18:0,
d18:3
|
DOI
|
Mollu
|
Lingula
unguis
|
16:0,18:0,
h16:0,h18:0,
d18:1,d18:3
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学・教育科学,45,31-42,1995
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
環形動物門
Annelida
|
貧毛綱
Oligochaeta
|
|
ミミズ
|
|
Pheretima
aspergillum
|
22:0,24:0,
h22:0,h23:0,
h24:0,br-d18:1,
d18:1,t18:0
|
DOI
|
Pheretima
aspergillum
|
22:0,24:0,
br-d18:1,
d18:1,
br-d19:1
|
DOI
|
Pheretima
aspergillum
(Galβ1-6Galβ1-Cer)
Pheretima
hilgendorfi
(PC-6Galβ1
-6Galβ1-Cer)
|
22:0,24:0,
h24:0,
br-d18:1,
d18:1,t18:0
22:0,24:0,
br-d18:1,
br-d19:1
|
DOI
PubMed
|
Neogala
|
|
|
|
|
|
(*環形動物門では
SMは見つからない。)
PubMed
(*SM-Binding Protein, Lyseninはミミズから抽出。)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ヒル綱
Hirudinea
|
|
ヒル
|
Hirudo
nipponica
(β-GalCer)
|
16:0,22:0,
24:0,d18:1,
br-d19:1,
d22:3
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
Hirudo
nipponica
(Galα1-6Galβ1-Cer,
PC-6Galβ1
-6Galβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,22:0,
24:0,d18:1,
br-d19:1,
16:0,22:0,
24:0,t18:0,
br-t19:0,
d22:3
|
DOI
|
Isoneogala
|
|
|
|
|
|
(*環形動物門ではSMは見つからない。)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
多毛綱
Polychaeta
|
サシバゴカイ目
Phyllodocida
|
イトメ
|
Tylorrhynchus
heterochaetus
|
16:0,17:0,
18:0,h16:0,
h17:0 d18:1,
d18:2
|
DOI
|
Tylorrhynchus
heterochaetus
|
16:0,17:0,
18:0,h16:0,
h17:0
|
DOI
|
Tylorrhynchus
heterochaetus
(PC-6Galβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,d18:1,
d18:2
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(*環形動物門ではSMは見つからない。)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tylorrhynchus
heterochaetus
(InsMe-P-Cer)
|
h16:0,h18:0,
t18:0
|
DOI
|
ケヤリ目
Sabellida
|
エラコ
|
Pseudopotamilla
occelata
|
16:0,18:0,
h16:0,h18:0,
d18:1
|
DOI
|
Pseudopotamilla
occelata
|
16:0,18:0,
h16:0,h18:0,
d18:1
|
DOI
|
Pseudopotamilla
occelata
(Galα1-4Galβ1-Cer,
Galβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,18:0,
d18:1,
20:1,22:1,
d18:1
|
DOI
|
Gala
|
|
|
|
|
|
(*環形動物門ではSMは見つからない。)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pseudopotamilla
occelata
(Ins-P-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
軟体動物門
Mollusca
|
二枚貝綱
Bivalvia
|
|
二枚貝
|

|
Hyriopsis
schlegelii
/egg
|
14:0,16:0,
h16:0,d18:1,
br-d19:1
|
PubMed
|
Hyriopsis
schlegelii
/egg
|
14:0,16:0,
h16:0,d18:1,
br-d19:1
|
PubMed
|
Hyriopsis
schlegelii
/sperm
(Manα1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,18:0,
20:0,d18:1,
br-d18:1
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
Mollu
|
Pinctada
martensii
|
h16:0,h18:0,
d18:1,d18:0
|
PubMed
|
Pinctada
martensii
|
16:0,17:0,
18:0,d16:1,
d18:1,d18:2
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学,54,41-48,2004
|
Hyriopsis
schlegelii
/egg
|
15:0,16:0,
d18:1
|
DOI
|
Mytilus
galloprovincialis
|
16:0,h16:0,
d18:1,t18:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
腹足綱
Gastropoda
|
|
巻貝
|
Chlorostoma
argyrostoma
turbinatum
|
16:0,h16:0,
h18:0,d18:1,
d18:2
|
PubMed
|
Euhadra
hickonis
|
16:0,h16:0,
br-d19:1,
d18:1
|
DOI
|
Chlorostoma
argyrostoma
turbinatum
(Galβ1-6Galβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,17:0,
h16:0,h18:0,
d18:1,
br-d18:1,
d18:2,d19:1
|
PubMed
|
Neogala
|
Heterogen
longispira
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Sinotaia
historica
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Monodonta
labio
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Monodonta
labio
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
頭足綱
Cephalopoda
|
|
イカ、タコ
|
Ommastrephes
sloani pacificus
/sperm
|
16:0,18:0,
22:0,22:1,
d16:1
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学・教育科学,44,17-23,1994
|
Ommastrephes
sloani pacificus
/sperm
|
16:0,18:0,
22:0,22:1,
d16:1
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学・教育科学,44,17-23,1994
|
Ommastrephes
sloani pacificus
/sperm
(Manβ1-4Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Todarodes
pacificus
(GT3,GQ1c)
|
16:0,18:1,
22:1,24:1,
d16:1
undescribed
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学・教育科学,44,17-23,1994
PubMed
|
c-series
|
|
|
|
Todarodes
pacificu
/viscera
|
16:0,18:0,
24:1,d16:1
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学,59,29-37,2009
|
Todarodes
pacificus
/viscera
|
16:0,22:1,
24:1,d16:1
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学,59,29-37,2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(旧口動物、脱皮)
(Protostomia, Ecdysozoa)
|
線形動物門
Nematoda
|
クロマドラ綱
Chromadorea
|
|
回虫
|
|
|
|
|
Ascaris
suum
/adult
Ascaris
suum
|
h24:0,br-d17:1,
br-d17:0,
br-t17:0,t18:0
|
PubMed
DOI
|
Ascaris
suum
(HSO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
Ascaris
suum
/adult
(GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Ascaris
suum
(PC-6GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
24:0,h24:0,br-d17:1,
br-d17:0,
br-t18:0
h24:0,br-d17:1,
br-d17:0
h22:0,h24:0,
br-d17:1,
br-d17:0
|
PubMed
PubMed
DOI
|
Arthro
|
|
|
|
Ascaris
suum
|
24:0,h24:0,
br-d17:1,
br-d17:0,
br-t17:0
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ascaris
suum
(Galα1-
2Ins-P-Cer)
|
24:0,h24:0,
br-d17:0,
d18:0
|
PubMed
|
| 節足動物門 Arthropoda
|
昆虫綱 Insecta
|
|
ハエ
|

|
|
|
|
Lucilia
caesar
/larvae
|
16:0,18:0,
20:0,22:0,
d14:1,d16:1
|
PubMed
|
Lucilia
caesar
/larvae
(GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
16:0,18:0,
20:0,22:0,
d14:1,d16:1
|
PubMed
|
Arthro
|
Lucilia
caesar
/pupae
|
20:0,22:0
|
PubMed
(*昆虫綱ではショウジョウバエなど少数の種のみCPEを多くもつ。)
|
Aedes
aegypti
/cells
|
18:0,20:0,
22:0
|
PubMed
(*昆虫綱では多くの種がSMをもつ。)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
甲殻亜門
軟甲綱
Crustacea
Malacostraca
|
|
エビ、カニ
|
|
|
|
Penaeus
duorarum
/ventral nerve
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Euphausia
superba
(GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Euphausia
superba
(MAEPn-6Glcβ1-Cer)
|
22:1,24:1,
d14:1
22:1,h22:1,
h24:1,d14:1,
br-d18:3,
d18:3
|
DOI
PubMed
|
Arthro
|
|
|
|
Erimacrus
isenbeckii
|
18:0,20:0,
22:0,22:1,
d14:1,d14:0
|
滋賀大学教育学部紀要,自然科学,52,9-16,2002
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
甲殻亜門
鰓脚綱
Crustacea Branchiopoda
|
|
カブトエビ、ミジンコ
|
|
|
|
Artemia
franciscana
|
18:0,22:0,
h18:0,d16:1,
d17:1
|
PubMed
|
Artemia
franciscana
(GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
22:0,d16:1,
d17:1
|
PubMed
|
Arthro
|
|
|
|
Artemia
franciscana
|
18:0,22:0,
d16:1,d17:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
多足亜門
ヤスデ綱
Myriapoda Diplopoda
|
|
ヤスデ
|
|
|
|
Parafontaria
laminata
|
h(2- or 3-hydroxy)23:0,
h(2- or 3-hydroxy)24:0,
d17:1,br-d18:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Parafontaria
laminata
(GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
|
22:0,23:0,
24:0,d17:1,
br-d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Arthro
|
Parafontaria
laminata
|
16:0,17:0,
18:0,22:0,
d17:1,d18:1
|
滋賀文化短期大学紀要,3,71-78,1993
|
Spirostreptus
asthene s
/oocytes
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(新口動物)
(Deuterostomia)
|
棘皮動物門
Echinodermata
|
ウミユリ綱
Crinoidea
|
|
ウミユリ
|
|
|
|
|
Comanthus
japonica
|
24:0,h18:0,
h22:1,h24:0,
d16:1,d18:2,
t16:0
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comanthus
japonica
(Ins-P-Cer)
|
22:0,24:0,
d16:1
|
DOI
DOI
(*9-O-MeNeuGc
が結合したGIPC
がある。)
DOI
(*9-O-MeNeuAc
が結合したGIPC
がある。)
|
ヒトデ綱
Asteroidea
|
|
ヒトデ
|
Culcita
novaeguineae
|
h22:0,br-t16:0
|
PubMed
|
Asterias
rubens
|
d18:2,d22:1,
d22:2
|
PubMed
|
Luidia
maculata
(Galβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Luidia
maculata
((3-sulfo)Galβ1
-4Galβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer)
Luidia
maculata
(GM3)
Luidia
maculata
(GD3)
|
h16:0,h22:0,
h24:0,
br-d19:1,
t16:0,
br-t17:0,
t22:1
h22:0,
br-t19:0
h22:0,t19:0
h22:0,t17:0
|
DOI
DOI
DOI
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Distolasterias
nipon
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
クモヒトデ綱
Ophiuroidea
|
|
クモヒトデ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ophiocoma
scolopendrina
(NeuGcα2
-6Glcβ1-Cer,
GM5,
HSO3-8NeuAcα2
-6Glcβ1-Cer)
|
18:0,t18:0,
br-t18:0,
h22:0,t18:0,
br-t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Echino
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ウニ綱
Echinoidea
|
|
ウニ
|
|
|
|
Anthocidaris
crassispina
/egg
|
22:1,24:1,
h22:1,h24:1,
t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Anthocidaris
crassispina
/egg
(Galα1-6Glcβ1Cer)
Anthocidaris
crassispina
/egg
(NeuGcα2
-6Glcβ1-Cer,
GM5,
HSO3-8NeuGcα2
-6Glcβ1-Cer)
|
22:1,24:1,
h22:1,h24:1,
t18:0
h22:1,h23:1,
h24:1,t18:0
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
Echino
|
|
|
|
Strongylocentrotus
intermedius
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ナマコ綱
Holothuroidea
|
|
ナマコ
|
Bohadschia
argus
|
h24:1,d17:1,
br-d17:1
|
PubMed
|
Cucumaria
echinata
|
h22:0,h23:0,
h24:0,
br-d17:1
|
DOI
|
Holothuria
leucospilota
(NeuGcα2
-6Glcβ1-Cer,
GM5)
|
h22:0,h23:0,
h24:0,h24:1,
br-t17:0,br-t18:0,
br-t19:0
|
DOI
|
Echino
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
脊索動物門
Chordata
|
ホヤ綱
Ascidiacea
|
|
ホヤ
|
|
|
|
|
Aplidium
nordmani,
Styela
partita,
Botryllus
leachii
|
h24:0,t18:0,
br-t19:0
|
DOI
|
Microcosmus
sulcatus
(Galβ1-4(Fucα1
-3)Glcβ1-Cer)
|
h22:0,h23:0,
t19:0
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
Ciona
intestinalis
|
16:0,18:0,
18:1,d16:1,
d18:2
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
軟骨魚綱
Chondrichthyes
|
|
エイ
|

|
Carcharhinus
plumbeus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Squalus
acanthias
/rectal gland
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Bathyraja
smirnovi
(GM2,GD2)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Torpedo
marmorata
/electric organ
|
16:0,24:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
条鰭綱
Actinopterygii
|
|
硬骨魚
|
|
Cyprinus
carpio
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
24:1,h24:0
|
PubMed
|
Theragra
chalcogramm
/brain
|
24:1
|
PubMed
|
Latimeria
chalumnae
(GM3,GD3)
Theragra
chalcogramma
(9-O-Ac-GT3)
|
16:0,18:0,
24:1,d18:1
undescribed
|
DOI
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series,
c-series
|
|
|
|
Latimeria
chalumnae
/brain
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
両生綱
Amphibia
|
|
カエル
|

|
Rana
catesbeiana
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
18:0,24:1,
h24:1,d18:0,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Bufo
japonicus
/skin
|
22:0,24:0,
h22:0,h24:0,
t18:0
|
PubMed
|
Rana
pipiens
(GD1b,GT1b)
|
undescribed
|
DOI
|
b-series
|
|
|
|
Rana
pipiens
/spinal cord
|
undescribed
|
J.Exp.Biol. 29, 203-210, 1952
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
爬虫綱
Reptilias
|
|
ワニ
|

|
Iguana spp.
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
nonhydroxy FA,hydoroxy FA
|
PubMed
|
Anolis
carolinensis
/kidney
|
h23:0,h24:0,
h24:1,d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Pseudemys
scripta elegans
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b,GQ1b)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Tropidurus
torquatus
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
鳥綱
Aves
|
|
トリ
|
|
Gallus
gallus domesticus
/sciatic nerve
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
22:0,24:0,
h22:0,h24:0
|
PubMed
|
Gallus
gallus
domesticus
/lens
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Anser
anser
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b,GQ1b)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Colurnba
livia domestica
/liver
|
16:0,18:0,
20:4
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
哺乳綱
Mammalia
|
無盲腸目
Eulipotyphla
|
モグラ
|
|
Suncus
murinus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
24:0,h24:0,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Suncus
murinus
/brain
|
24:0,h24:0,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Suncus
murinus
/brain
(GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1
-4Glcβ1-Cer,
GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b)
|
24:0,d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Ganglio,
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Suncus
murinus
/liver
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
食肉目
Carnivora
|
ネコ、イヌ
|
Felis
silvestris catus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Canis
lupus familiaris
/intestine
|
20:0,22:0,
24:0,hFA
|
PubMed
|
Felis
silvestris catus
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b,GQ1b)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Canis lupus
familiaris
/brain
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
奇蹄目
Perissodactyla
|
ウマ
|
Equus
caballus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
22:0,24:0,
24:1,h22:0,
h24:0,h24:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Equus
caballus
/spleen
|
16:0,22:0,
24:0
|
PubMed
|
Equus
caballus
/brain
(GM4,GM3,GM2,
GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b)
|
18:0,20:0,
24:0,h24:0,
h24:1,d18:1,
d20:1
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Equus
caballus
/spinal cord
|
16:0,18:0,
22:0,24:1
|
DOI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
鯨偶蹄目
Cetartiodactyla
|
ウシ、ブタ
|
Bos
taurus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
18:0,24:0,
24:1,h18:0,
h24:0,h24:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Bos
taurus
/spleen
|
22:0,23:0,
24:0
|
PubMed
|
Bos
taurus
/brain
(GM2,GM1,GD3,
GD1a,GD1b)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Bos
taurus
/brain
|
18:0,24:0,24:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Ovis
aries
/brain,
Capra
linnaeus
/brain
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
兎目
Lagomorpha
|
ウサギ
|
Oryctolagus
cuniculus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Oryctolagus
cuniculus
/skin fibroblasts
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Oryctolagus
cuniculus
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Oryctolagus
cuniculus
/brain
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
齧歯目
Rodentia
|
ラット、マウス
|
Rattus
norvegicus
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
Mus
musculus
/erythrocytes
|
16:0,18:1,
22:0,24:1,
d18:1
|
PubMed
|
Rattus
norvegicus
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Rattus
norvegicus
/brain
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
霊長目
Primates
|
ヒト
|
|
Homo
sapiens
/brain
(Gal-Cer,SO3-3Galβ1-Cer)
|
18:0,24:1,
24:0,25:1,
25:0,26:1,
h16:0,h22:0,
h23:0,h24:1,
h24:0
|
PubMed
|
Homo
sapiens
/spleen of
Gaucher's
disease
Homo
sapiens
/blood
|
22:0,d18:1
undescribed
|
PubMed
PubMed
|
Homo
sapiens
/brain
(GM1,GD1a,GD1b,
GT1b)
|
undescribed
|
PubMed
|
a-series,
b-series
|
|
|
|
Homo
sapiens
/brain
|
18:0,24:1
|
PubMed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
In Mammalia, GlcCer is synthesized by ceramide glucosyltransferase (CGlcT) at the cytosolic membrane of the Golgi apparatus, and GalCer is synthesized by ceramide galactosyltransferase (CGalT) at the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). These enzymes do not share any sequence similarity and CGlcT possesses its transmembrane region at the N-terminal (type III) whereas CGalT possesses it at the C-terminal (type I).[1]
|
哺乳動物では、ゴルジ装置の細胞質側に局在するグルコシルセラミド合成酵素(CGlcT)によって GlcCer が、小胞体の内腔側に局在するガラクトシルセラミド合成酵素(CGalT)によって GalCer が作られます。これらの酵素は配列相同性が無く、CGlcT は膜貫通領域が N 末端側(III型酵素)、CGalT は C 末端側(I型酵素)です。
|
|
|
GlcCer |
GalCer
|
| Enzyme
|
CGlcT (EC 2.4.1.80)
|
CGalT (EC 2.4.1.45)
|
| Reaction
|
Ceramide + UDP-glucose → GlcCer + UDP
|
Ceramide + UDP-galactose → GalCer + UDP
|
| Location
|
Golgi (outside) → flipflop → Golgi (inside)
|
ER lumen
|
Since all glycolipid synthesizing enzymes (except for CGlcT and CGalT) reside at the lumen of the Golgi apparatus, GlcCer must be flip-flopped from the cytosolic side to the lumen by an eyzyme called flippase.
To synthesize GalCer, UDP-galactose and ceramide must transport the ER membrane. UDP-galactose transporter 2 (UGT2) is considered to be responsible.
GalT can also work on glycerolipid, and synthsizes sulfated glyceroglycolipid in mammalian testis, called seminolipid.
|
CGlcT, CGalT 以外の糖脂質合成酵素はゴルジ装置の内腔側にあり、GlcCer はゴルジ膜の細胞質側から内腔側にフリッパーゼと呼ばれる酵素で移動(フリップフロップ)します。GalCer の場合は、UDPガラクトースとセラミドが小胞体膜を通過します。UDPガラクトーストランスポータ2 (UGT2) が関与するようです。
CGalTはグリセロ脂質にも作用し、精巣の硫酸化グリセロ糖脂質であるセミノリピドも合成します。
|
- ↑ Sprong H, Degroote S, Nilsson T, Kawakita M, Ishida N, van der Sluijs P, van Meer G "Association of the Golgi UDP-galactose transporter with UDP-galactose:ceramide galactosyltransferase allows UDP-galactose import in the endoplasmic reticulum" Mol Biol Cell. 2003;4:3482-93 PMID 12925779
|