LBF22603SC01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Lipid/Header}} | |||
{{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | {{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 4: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=DFA0224 | |LipidBank=DFA0224 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA01030185 | |LipidMaps=LMFA01030185 | ||
|SysName=cis-4, cis-7, cis-10, cis-13, cis-16, cis-19-Docosahexaenoic acid | |SysName=(cis-4,cis-7,cis-10,cis-13,cis-16,cis-19) -Docosahexaenoic acid | ||
|Common Name=&& | |Common Name=&&DHA&&Cervonic acid&&(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z) -Docosahexaenoic acid&& | ||
|Melting Point=-44.2 to -44.1 °C | |Melting Point=-44.2 to -44.1 °C | ||
| | |Refractive=1.5017 at 26 °C | ||
|Solubility=soluble in benzene, chloroform, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether. | |Solubility=soluble in benzene, chloroform, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether.[[Reference:Klenk_E:Bongard_W:,Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.,1952,291,104|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Klenk_E:Bongard_W:,Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.,1952,291,104}}]][[Reference:Klenk_E:Lindlar_F:,Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.,1955,299,74|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Klenk_E:Lindlar_F:,Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.,1955,299,74}}]][[Reference:Whitcutt_JM:,Biochem. J.,1957,67,60|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Whitcutt_JM:,Biochem. J.,1957,67,60}}]] | ||
|Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF22603SC01CH0002.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | |Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF22603SC01CH0002.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | ||
|Source=South African pilchard oil; brain phosphatides; liver lipids of cattle. It is found mainly in fish and marine microorganisms and plants. DHA is also an essential component of the brain, eyes, and other nervous system tissues. Tuna eyeballs are one of the major source <!--2012-->. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis= | |||
|Metabolism=Metabolic product of alpha -linolenic acid (9,12,25-18:3). The synthesis of 4,7,10,13,16,19-22:6 (=DHA) occurs via the following reaction sequence [[Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471}}]]: 9,12,15-18:3 --> 6,9,12,15-18:4 --> 8,11,14,17-20:4 --> 5,8,11,14,17-20:5 --> 7,10,13,16,19-22:5 --> 9,12,15,18,21-24:5 --> 6,9,12,15,18,21-24:6 --> 4,7,10,13,16,19-22:6. According to these pathways the 24-carbon acids that are made in the endoplasmic reticulum move to a site for partial beta-oxidation, which is most likely peroxisomes. | |||
|Symbol=DHA / C22:6n-3 / C22:6 omega 3 | |||
|Biological Activity=DHA is one of the n-3 ( omega 3) fatty acids. It is uniquely rich in neural membranes of retina and brain in mammals. n-3 fatty acid deficiency causes the reduction of DHA level in these tissues and produces reduced learning ability [[Reference:Yamamoto_N:Saitoh_M:Moriuchi_A:Nomura_M:Okuyama_H:,J. Lipid. Res.,1987,28,144|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Yamamoto_N:Saitoh_M:Moriuchi_A:Nomura_M:Okuyama_H:,J. Lipid. Res.,1987,28,144}}]], impaired vision, abnormal electroretinogram [[Reference:Neuringer_M:Connor_WE:Van_Petten_C:Barstad_L:,J. Clin. Invest.,1984,73,272|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Neuringer_M:Connor_WE:Van_Petten_C:Barstad_L:,J. Clin. Invest.,1984,73,272}}]][[Reference:Neuringer_M:Connor_WE:Lin_DS:Barstad_L:Luck_S:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1986,83,4021|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Neuringer_M:Connor_WE:Lin_DS:Barstad_L:Luck_S:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1986,83,4021}}]] and polydipsia [[Reference:Reisbick_S:Neuringer_M:Hasnain_R:Connor_WE:,Physiol. Behav.,1990,47,315|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Reisbick_S:Neuringer_M:Hasnain_R:Connor_WE:,Physiol. Behav.,1990,47,315}}]]. It is believed to be important for the full development of the nervous system in the fetus and newborn.[[Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409}}]] <http://www.focusnewsletter.org/dha.htm> <http://www.flax.com/library/Default.htm> Considered, along with EPA, to be the major reason for the beneficial effects of fish oils on the cardiovascular system. <http://www.omegadha.com/pages/dhastory.htm> Anti-inflammatory [[Reference:Tomobe_YI:Morizawa_K:Tsuchida_M:Hibino_H:Nakano_Y:Tanaka_Y:,Lipids,2000,35,61|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Tomobe_YI:Morizawa_K:Tsuchida_M:Hibino_H:Nakano_Y:Tanaka_Y:,Lipids,2000,35,61}}]][[Reference:Horrocks_LA:Yeo_YK:,Pharmacol. Res.,1999,40,211|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horrocks_LA:Yeo_YK:,Pharmacol. Res.,1999,40,211}}]][[Reference:Shikano_M:Masuzawa_Y:Yazawa_K:,J. Immunol.,1993,150,3525|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Shikano_M:Masuzawa_Y:Yazawa_K:,J. Immunol.,1993,150,3525}}]], anti-thrombotic [[Reference:Nieuwenhuys_CM:Hornstra_G:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1998,1390,313|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Nieuwenhuys_CM:Hornstra_G:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1998,1390,313}}]], anti-arteriosclerosis [[Reference:Horrocks_LA:Yeo_YK:,Pharmacol. Res.,1999,40,211|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horrocks_LA:Yeo_YK:,Pharmacol. Res.,1999,40,211}}]][[Reference:Connor_WE:DeFrancesco_CA:Connor:SL:,Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.,1993,683,16|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Connor_WE:DeFrancesco_CA:Connor:SL:,Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.,1993,683,16}}]] and anti-cancer activities [[Reference:Oshima_M:Takahashi_M:Oshima_H:Tsutsumi_M:Yazawa_K:Sugimura_T:Nishimura_S:Wakabayashi_K:Taketo_MM:,Carcinogenesis,1995,16,2605|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Oshima_M:Takahashi_M:Oshima_H:Tsutsumi_M:Yazawa_K:Sugimura_T:Nishimura_S:Wakabayashi_K:Taketo_MM:,Carcinogenesis,1995,16,2605}}]][[Reference:Takahashi_M:Minamoto_T:Yamashita_N:Kato_T:Yazawa_K:Esumi_H:,Cancer Lett.,1994,83,177|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Takahashi_M:Minamoto_T:Yamashita_N:Kato_T:Yazawa_K:Esumi_H:,Cancer Lett.,1994,83,177}}]] have been reported. Production of bioactive metabolites, eicosanoids, is suppressed by DHA. DHA can be also involved in the modulation of membrane structures [[Reference:Applegate_KR:Glomset_JA:,J. Lipid. Res.,1991,32,1645|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Applegate_KR:Glomset_JA:,J. Lipid. Res.,1991,32,1645}}]][[Reference:Applegate_KR:Glomset_JA:,J. Lipid. Res.,1991,32,1635|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Applegate_KR:Glomset_JA:,J. Lipid. Res.,1991,32,1635}}]]. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | |||
Latest revision as of 09:11, 21 July 2016
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0224 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030185 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF22603SC01 |
| DHA | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
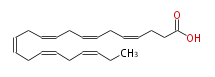
| (cis-4,cis-7,cis-10,cis-13,cis-16,cis-19) -Docosahexaenoic acid | |
| |
| DHA / C22:6n-3 / C22:6 omega 3 | |
| Formula | C22H32O2 |
| Exact Mass | 328.240230268 |
| Average Mass | 328.48828000000003 |
| SMILES | C(CCC(O)=O)=CCC=CCC=CCC=CCC=CCC=CCC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| -44.2 to -44.1 °C | |
| 1.5017 at 26 °C | |
| soluble in benzene, chloroform, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether. KlenkEet al. KlenkEet al. Whitcutt_JM | |
| South African pilchard oil; brain phosphatides; liver lipids of cattle. It is found mainly in fish and marine microorganisms and plants. DHA is also an essential component of the brain, eyes, and other nervous system tissues. Tuna eyeballs are one of the major source . | |
| Metabolic product of alpha -linolenic acid (9,12,25-18:3). The synthesis of 4,7,10,13,16,19-22:6 (=DHA) occurs via the following reaction sequence Sprecher_H et al.: 9,12,15-18:3 --> 6,9,12,15-18:4 --> 8,11,14,17-20:4 --> 5,8,11,14,17-20:5 --> 7,10,13,16,19-22:5 --> 9,12,15,18,21-24:5 --> 6,9,12,15,18,21-24:6 --> 4,7,10,13,16,19-22:6. According to these pathways the 24-carbon acids that are made in the endoplasmic reticulum move to a site for partial beta-oxidation, which is most likely peroxisomes. | |
| DHA is one of the n-3 ( omega 3) fatty acids. It is uniquely rich in neural membranes of retina and brain in mammals. n-3 fatty acid deficiency causes the reduction of DHA level in these tissues and produces reduced learning ability Yamamoto_N et al., impaired vision, abnormal electroretinogram Neuringer_M et al. Neuringer_M et al. and polydipsia Reisbick_S et al.. It is believed to be important for the full development of the nervous system in the fetus and newborn. Okuyama_H et al. <http://www.focusnewsletter.org/dha.htm> <http://www.flax.com/library/Default.htm> Considered, along with EPA, to be the major reason for the beneficial effects of fish oils on the cardiovascular system. <http://www.omegadha.com/pages/dhastory.htm> Anti-inflammatory Tomobe_YI et al. Horrocks_LA et al. Shikano_M et al., anti-thrombotic Nieuwenhuys_CM et al., anti-arteriosclerosis Horrocks_LA et al. Connor_WE et al. and anti-cancer activities Oshima_M et al. Takahashi_M et al. have been reported. Production of bioactive metabolites, eicosanoids, is suppressed by DHA. DHA can be also involved in the modulation of membrane structures Applegate_KR et al. Applegate_KR et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | Gas liquid chromatogram 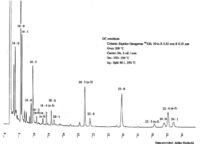 (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). |