LBF18306SC02: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Lipid/Header}} | |||
{{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | {{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 4: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=DFA0180 | |LipidBank=DFA0180 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA01030141 | |LipidMaps=LMFA01030141 | ||
|SysName=cis-6, cis-9, cis-12-Octadecatrienoic acid | |SysName=(cis-6,cis-9,cis-12) -Octadecatrienoic acid | ||
|Common Name=&& | |Common Name=&&(6Z,9Z,12Z) -Octadecatrienoic acid&&gamma-Linolenic acid&& | ||
|Melting Point=-11.3 to -11°C | |Melting Point=-11.3 to -11°C | ||
|Boiling Point=125°C at 0.05mmHg | |Boiling Point=125°C at 0.05mmHg | ||
|Density= | |Density=d^{20}_4 0.9164 | ||
| | |Refractive=1.4800 at 20°C | ||
|Solubility=soluble in acetone, ether, | |Solubility=soluble in acetone, ether, methyl alcohol and petroleum ether.<!--0352--><!--0383--><!--0415--> | ||
|Source=Isolated from seeds of Oenothera biennis and O. lamarckiana (evening primroses); drying oils. A minor component of many animal lipids. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis= | |||
|Metabolism=Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is synthesized from oleic acid (18:1n-9) by desaturation of Delta 12-desaturase, and alpha -linolenic acid (18:3n-3) is formed from linoleic acid by desaturation reaction of Delta 15-desaturase. Since both Delta 12- and 15-desaturases are present in plant cells but not in animal cells, linoleic and alpha -linolenic acid are not biosynthesized in animal cells in vivo. When ingested by animals, linoleic acid is desaturated, elongated to form gamma -linolenic acid (18:3n-6), dihomo- gamma -linolenic acid (20:3n-6), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) and adrenic acid (22:4n-6). Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-6) is synthesized from adrenic acid in significant amounts only under conditions of prolonged n-3 fatty acid deficiency., No interconversion between the n-6 and n-3 series in mammals. Nutritionally, it is important to note that different foods contain different proportions of n-6/n-3 and therefore the n-6/n-3 ratio in tissue lipids change significantly depending on the choice of foods.[[Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Okuyama_H:Kobayashi_T:Watanabe_S:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1996,35,409}}]] | |||
|Symbol=C18:3n-6 / C18:3 omega 6 / gamma Lnn / gamma LnA | |||
|Biological Activity=There are two groups of essential fatty acids, the n-6 (or omega 6) and the n-3 (or omega 3). gamma -linolenic acid is n-6 fatty acids. Essential fatty acid deficiency causes skin lesion and growth retardation. Dietary supplementation of either linoleate, gamma -linoleate or arachidonate prevents such symptoms completely. The n-6 essential fatty acids have at least four roles [[Reference:Horrobin_DF:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1992,31,163|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horrobin_DF:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1992,31,163}}]]: 1) Modulation of membrane structure. 2) Formation of short-lived giologically active molecules. Oxygenated derivatives of gamma -linolenic acid is a Arachidonic acid may have a role in the regulation of cell devision in cancer and other cells. There are other bioactive substance, PGE1 and 15-OH-dihomogamma-linolenic acid which are both formed from gamma -linolenic acid after its rapid elongation to dihomogamma-linolenic acid. 3) Control of the water impermeability of the skin. 4) Regulation of cholesterol synthesis and transport. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | |||
Latest revision as of 19:45, 1 October 2010
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0180 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030141 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF18306SC02 |
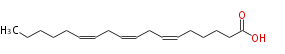
| (6Z,9Z,12Z) -Octadecatrienoic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
| (cis-6,cis-9,cis-12) -Octadecatrienoic acid | |
| |
| C18:3n-6 / C18:3 omega 6 / gamma Lnn / gamma LnA | |
| Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Exact Mass | 278.224580204 |
| Average Mass | 278.4296 |
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCCC(O)=O |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| -11.3 to -11°C | |
| 125°C at 0.05mmHg | |
| d20 4 0.9164 | |
| 1.4800 at 20°C | |
| soluble in acetone, ether, methyl alcohol and petroleum ether. | |
| Isolated from seeds of Oenothera biennis and O. lamarckiana (evening primroses); drying oils. A minor component of many animal lipids. | |
| Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is synthesized from oleic acid (18:1n-9) by desaturation of Delta 12-desaturase, and alpha -linolenic acid (18:3n-3) is formed from linoleic acid by desaturation reaction of Delta 15-desaturase. Since both Delta 12- and 15-desaturases are present in plant cells but not in animal cells, linoleic and alpha -linolenic acid are not biosynthesized in animal cells in vivo. When ingested by animals, linoleic acid is desaturated, elongated to form gamma -linolenic acid (18:3n-6), dihomo- gamma -linolenic acid (20:3n-6), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) and adrenic acid (22:4n-6). Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-6) is synthesized from adrenic acid in significant amounts only under conditions of prolonged n-3 fatty acid deficiency., No interconversion between the n-6 and n-3 series in mammals. Nutritionally, it is important to note that different foods contain different proportions of n-6/n-3 and therefore the n-6/n-3 ratio in tissue lipids change significantly depending on the choice of foods. Okuyama_H et al. | |
| There are two groups of essential fatty acids, the n-6 (or omega 6) and the n-3 (or omega 3). gamma -linolenic acid is n-6 fatty acids. Essential fatty acid deficiency causes skin lesion and growth retardation. Dietary supplementation of either linoleate, gamma -linoleate or arachidonate prevents such symptoms completely. The n-6 essential fatty acids have at least four roles Horrobin_DF : 1) Modulation of membrane structure. 2) Formation of short-lived giologically active molecules. Oxygenated derivatives of gamma -linolenic acid is a Arachidonic acid may have a role in the regulation of cell devision in cancer and other cells. There are other bioactive substance, PGE1 and 15-OH-dihomogamma-linolenic acid which are both formed from gamma -linolenic acid after its rapid elongation to dihomogamma-linolenic acid. 3) Control of the water impermeability of the skin. 4) Regulation of cholesterol synthesis and transport. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|