LBF20207PG25: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=XPR1501 | |LipidBank=XPR1501 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA03010002 | |LipidMaps=LMFA03010002 | ||
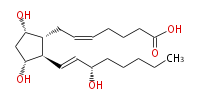
|SysName=7- [ | |SysName=7- [ (3R,5S) -Dihydroxy-2R - (3S -hydroxy-trans-1-octenyl) cyclopentan-1R -yl] -cis-5-heptenoic acid | ||
|Common Name=&&Prostaglandin | |Common Name=&&Prostaglandin F_2 alpha&&7- [ 3 (R) ,5 (S) -Dihydroxy-2 (R) - (3 (S) -hydroxy-1 (E) -octenyl) cyclopentan-1 (R) -yl ] -5 (Z) -heptenoic acid&& | ||
|Melting Point=25-35°C [[Reference:Bundy_GL:Schneider_WP:Lincoln_FH:Pike_JE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1972,94,2123|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bundy_GL:Schneider_WP:Lincoln_FH:Pike_JE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1972,94,2123}}]] | |Melting Point=25-35°C [[Reference:Bundy_GL:Schneider_WP:Lincoln_FH:Pike_JE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1972,94,2123|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bundy_GL:Schneider_WP:Lincoln_FH:Pike_JE:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1972,94,2123}}]] | ||
|Optical=[ alpha ]^{25}_D =23.8 °(C=1,THF) [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397}}]] | |Optical=[ alpha ]^{25}_D =23.8 °(C=1,THF) [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397}}]] | ||
|Solubility= ETHYL ACETATE, ACETONE, DIETHYLETHER [[Reference: | |Solubility= ETHYL ACETATE, ACETONE, DIETHYLETHER [[Reference:Pike_JE:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Pike_JE:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552}}]]. STABILITIES: to be stable under neutral and basic conditions [[Reference:Karim_SM:Devlin_J:Hillier_K:,Eur. J. Pharmacol.,1968,4,416|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Karim_SM:Devlin_J:Hillier_K:,Eur. J. Pharmacol.,1968,4,416}}]] | ||
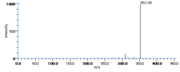
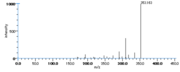
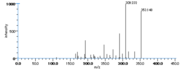
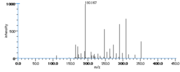
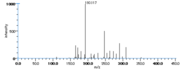
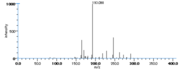
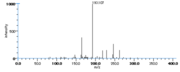
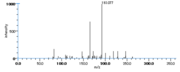
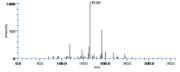
|Mass Spectra=354(M^+ ), 336, 318, 292, 274, 264(100), 247, 229, 191, 177, 165, 137, 99, 81, 67 [[Reference:Horvath_G:,Biomed. Mass Spectrom.,1976,3,127|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horvath_G:,Biomed. Mass Spectrom.,1976,3,127}}]] | |Mass Spectra=354(M^+ ), 336, 318, 292, 274, 264(100), 247, 229, 191, 177, 165, 137, 99, 81, 67 [[Reference:Horvath_G:,Biomed. Mass Spectrom.,1976,3,127|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horvath_G:,Biomed. Mass Spectrom.,1976,3,127}}]] | ||
|IR Spectra=NEAT : 3320, 2640, 1710, 1295, 1260, 1245, 1120, 1080, 1055, 1025, 975cm^{-1} [[Reference: | |IR Spectra=NEAT : 3320, 2640, 1710, 1295, 1260, 1245, 1120, 1080, 1055, 1025, 975cm^{-1} [[Reference:Pike_JE:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:PikeJ_E:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552}}]] | ||
|NMR Spectra=^1 H-NMR(d_6 -ACETONE) : delta 5.48(m, 4H), 4.05(m, 3H), 0.9(t, 3H, 20-CH3) [[Reference: | |NMR Spectra=^1 H-NMR(d_6 -ACETONE) : delta 5.48(m, 4H), 4.05(m, 3H), 0.9(t, 3H, 20-CH3) [[Reference:Pike_JE:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Pike_JE:Lincoln_FH:Schneider_WP:,J. Org. Chem.,1969,34,3552}}]]. ^{13}C-NMR : 176.6(C1), 135.0(C14), 132.8(C5), 129.1(C13 or C6), 128.9(C6 or C13), 77.2(C11), 72.9(C15), 71.8(C9), 55.0(C12), 49.9(C8), 42,6(C10), 36.8(C16), 33.2(C2), 31,5(C18), 26.3(C4), 25.1(C7), 25.1(C17), 24.5 [[Reference:Lukacs_G:Piriou_F:Gero_SD:,Tetrah. Lett.,1973,,515|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Lukacs_G:Piriou_F:Gero_SD:,Tetrah. Lett.,1973,,515}}]] | ||
|Source=Prostaglandin F2 alpha was found to be accummulating in human semen in an amount of about 2 microgram per ml [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382}}]]. In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin F2 alpha . | |Source=Prostaglandin F2 alpha was found to be accummulating in human semen in an amount of about 2 microgram per ml [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382}}]]. In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin F2 alpha . | ||
|Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397}}]] {{Image200|LBF20207PG25FT0001.gif}} | |Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Schaaf_TK:Huber_W:Koelliker_U:Weinshenker_NM:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1970,92,397}}]] {{Image200|LBF20207PG25FT0001.gif}} | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|Biological Activity=Prostaglandin F2 alpha exhibits various biological activities such as uterine contraction, gastrointestinal contraction, bronchoconstriction, luteolysis and vasoconstriction [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]]. Prostaglandin F2 alpha is a ligand to a receptor (FP) present in the cell membrane [[Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109}}]]. | |Biological Activity=Prostaglandin F2 alpha exhibits various biological activities such as uterine contraction, gastrointestinal contraction, bronchoconstriction, luteolysis and vasoconstriction [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]]. Prostaglandin F2 alpha is a ligand to a receptor (FP) present in the cell membrane [[Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109}}]]. | ||
|Genetic Information=cDNA for prostaglandin F synthase was cloned from bovine lung [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]]. cDNA for prostaglandin F2 alpha receptor (FP) was cloned, and its 7ptransmembrane structure was reported [[Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109}}]]. | |Genetic Information=cDNA for prostaglandin F synthase was cloned from bovine lung [[Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Urade_Y:Watanabe_K:Hayaishi_O:,J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal.,1995,12,257}}]]. cDNA for prostaglandin F2 alpha receptor (FP) was cloned, and its 7ptransmembrane structure was reported [[Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Negishi_M:Sugimoto_Y:Ichikawa_A:,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1995,1259,109}}]]. | ||
}} | |||
{{MassbankSpectra| | |||
UT000352 | |||
UT000353 | |||
UT000354 | |||
UT000355 | |||
UT000356 | |||
UT000357 | |||
UT000358 | |||
UT000359 | |||
UT000360 | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:00, 17 January 2014
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1501 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010002 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20207PG25 |
| Prostaglandin F2α | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
| 7- [ (3R,5S) -Dihydroxy-2R - (3S -hydroxy-trans-1-octenyl) cyclopentan-1R -yl] -cis-5-heptenoic acid | |
| |
| PGF2α | |
| Formula | C20H34O5 |
| Exact Mass | 354.240624198 |
| Average Mass | 354.48096000000004 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](O)C=C[C@H]([C@H]1CC=CCCCC(O)=O)[C@@H](C[C@@H]1O)O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 25-35°C Bundy_GL et al. | |
| [ α ]25 D =23.8 °(C=1,THF) Corey_EJ et al. | |
| ETHYL ACETATE, ACETONE, DIETHYLETHER Pike_JE et al.. STABILITIES: to be stable under neutral and basic conditions Karim_SM et al. | |
| Prostaglandin F2 alpha was found to be accummulating in human semen in an amount of about 2 microgram per ml Bergstrom_S . In most animal tissues prostanoids are synthesized enzymatically de novo upon physiological and pathological stimulations, and this is also the case of prostaglandin F2 alpha . | |
|
Corey_EJ et al. | |
| Prostaglandin F synthase reduces 9,11-endoperoxide of prostaglandin H2 requiring NADPH, and produces prostaglandin F2 alpha . The same enzyme also reduces 9-keto group of prostaglandin D2 producing 11 beta -prostaglandin F2 Urade_Y et al.. | |
| Prostaglandin F2 alpha exhibits various biological activities such as uterine contraction, gastrointestinal contraction, bronchoconstriction, luteolysis and vasoconstriction Bergstrom_S et al.. Prostaglandin F2 alpha is a ligand to a receptor (FP) present in the cell membrane Negishi_M et al.. | |
| cDNA for prostaglandin F synthase was cloned from bovine lung Urade_Y et al.. cDNA for prostaglandin F2 alpha receptor (FP) was cloned, and its 7ptransmembrane structure was reported Negishi_M et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | 354(M+), 336, 318, 292, 274, 264(100), 247, 229, 191, 177, 165, 137, 99, 81, 67 HorvathG |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | NEAT : 3320, 2640, 1710, 1295, 1260, 1245, 1120, 1080, 1055, 1025, 975cm-1 PikeJEet al. |
| NMR Spectra | 1H-NMR(d6-ACETONE) : δ 5.48(m, 4H), 4.05(m, 3H), 0.9(t, 3H, 20-CH3) Pike_JE et al.. 13C-NMR : 176.6(C1), 135.0(C14), 132.8(C5), 129.1(C13 or C6), 128.9(C6 or C13), 77.2(C11), 72.9(C15), 71.8(C9), 55.0(C12), 49.9(C8), 42,6(C10), 36.8(C16), 33.2(C2), 31,5(C18), 26.3(C4), 25.1(C7), 25.1(C17), 24.5 LukacsGet al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|