LBF20407LX01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=DFA8153 | |LipidBank=DFA8153 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA03040001 | |LipidMaps=LMFA03040001 | ||
|SysName=5S,6R,15S- | |CAS=89663-86-5 | ||
|Common Name=&& | |SysName=(5S,6R,15S) -Trihydroxy- (trans-7,trans-9,cis-11,trans-13) -eicosatetraenoic acid | ||
|UV Spectra=< | |Common Name=&&Lipoxin A_4&&(5S,6R,15S) -Trihydroxy- (7E,9E,11Z,13E) -eicosatetraenoic acid&& | ||
|Source=LXA4 is formed in vitro by a number of mechanisms from arachidonic acid, 15-HpETE, and leukotriene A4 (LTA4 ) [[Reference:Edenius_C:Stenke_L:Lindgren_JA:,Eur. J. Biochem.,1991,199,401|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Edenius_C:Stenke_L:Lindgren_JA:,Eur. J. Biochem.,1991,199,401}}]][[Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335}}]]. | |Solubility=diethyl ether, methanol. [[Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464}}]]<!--1037--> | ||
|Chemical Synthesis= | |UV Spectra=lambda max: 302nm epsilon : 50,000, lambda MeOHmax: 287,301 (epsilon 50,000) : 316nm [[Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464}}]]<!--1037-->, [[Reference:Serhan_CN:Nicolaou_KC:Webber_SE:Veale_CA:Dahlen_SE:Puustinen_TJ:Samuelsson_B:,J._Biol._Chem.,1986,261,16340|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Nicolaou_KC:Webber_SE:Veale_CA:Dahlen_SE:Puustinen_TJ:Samuelsson_B:,J._Biol._Chem.,1986,261,16340}}]]<!--1038--> | ||
|Metabolism= | |NMR Spectra=^1 H-NMR(250MHz, 5% CD3OD/D2O ) : delta 0.8-0.9(brt, 3H), 1.2-1.8(m, 14H), 2.1-2.3(m, 2H), 3.4-3.6(m, 1H), 3.95-4.05(t, J=6.8Hz, 1H), 4.1-4.2(q, J=7.1Hz, 1H), 5.6-5.85(seven lines, 2H), 5.9-6.1(m, 2H), 6.2-6.45(m, 2H), 6.6-6.8(m, 2H). [[Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464}}]]<!--1037--> | ||
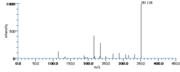
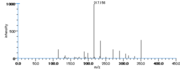
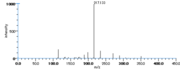
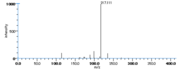
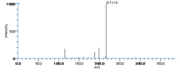
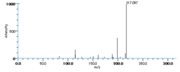
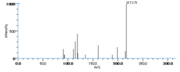
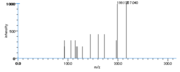
|Mass Spectra=TMS-derivs. ; 582(M^+ ), 492, 482, 379, 289, 203, 173, 171. [[Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Biochem._Biophys._Res._Commun.,1984,118,943|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Biochem._Biophys._Res._Commun.,1984,118,943}}]]<!--1036--> | |||
|Source=LXA4 is formed in vitro by a number of mechanisms from arachidonic acid, 15-HpETE, and leukotriene A4 (LTA4 ) [[Reference:Edenius_C:Stenke_L:Lindgren_JA:,Eur. J. Biochem.,1991,199,401|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Edenius_C:Stenke_L:Lindgren_JA:,Eur. J. Biochem.,1991,199,401}}]][[Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335}}]]. Lipoxin A4 is produced by activated leukocytes [[Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1}}]]<!--0035-->, [[Reference:Brady_HR:Serhan_CN:,Curr._Opin._Nephrol._Hypertens.,1996,5,20|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Brady_HR:Serhan_CN:,Curr._Opin._Nephrol._Hypertens.,1996,5,20}}]]<!--0036-->. | |||
|Chemical Synthesis=[http://lipidbank.jp/image/XPR4001FT0001.gif Table0001] [[Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Adams_J:Fitzsimmons_BJ:Girard_Y:Leblanc_Y:Evans_JF:Rokach_J:,J._Am._Chem._Soc.,1985,107,464}}]]<!--1037--> | |||
|Metabolism=Dual lipoxygenation pathways are considered for lipoxin A4 synthesis from arachidonic acid; either 15-lipoxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase in leukocytes or 5-lipoxygenase in leukocytes and 12-lipoxygenase in platelets [[Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1}}]]<!--0035-->. | |||
|Genetic Information=cDNA for a receptor specific for lipoxin A4 was cloned out of orphan cDNAs [[Reference:Fiore_S:Maddox_JF:Perez_HD:Serhan_CN:,J._Exp._Med.,1994,180,253|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Fiore_S:Maddox_JF:Perez_HD:Serhan_CN:,J._Exp._Med.,1994,180,253}}]]<!--0037-->. | |||
|Symbol=LXA4 | |||
|Biological Activity=LXA is equipotent to LTB in inducing superoxide generation in human neutrophils (0.1 mu M) [[Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335}}]]. LXA4 is associated with several other biological functions including leukocyte activation, chemotaxis promotion, natural killer cell inhibition, and monocyte migration and adhesion [[Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,1984,81,5335}}]][[Reference:Ramstedt_U:Serhan_CN:Nicolaou_KC:Webber_SE:Wigzell_H:Samuelsson_B:,J. Immunol.,1987,138,266|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Ramstedt_U:Serhan_CN:Nicolaou_KC:Webber_SE:Wigzell_H:Samuelsson_B:,J. Immunol.,1987,138,266}}]][[Reference:Maddox_JF:Serhan_CN:,J. Exp. Med.,1996,183,137|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Maddox_JF:Serhan_CN:,J. Exp. Med.,1996,183,137}}]]. Lipoxin A4 is either vasoconstrictive or vasodilatory, and has immunoregulatory activities blocking the cytotoxic action of NK cell, inhibiting adherence and chemotaxis of leukocytes induced by FMLP, PAF or leukotriene B4[[Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Serhan_CN:,Biochim._Biophys._Acta,1994,1212,1}}]]<!--0035-->. | |||
}} | |||
{{MassbankSpectra| | |||
UT000325 | |||
UT000326 | |||
UT000327 | |||
UT000328 | |||
UT000329 | |||
UT000330 | |||
UT000331 | |||
UT000332 | |||
UT000333 | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:00, 21 January 2014
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA8153 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03040001 |
| CAS | 89663-86-5 |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20407LX01 |
| Lipoxin A4 | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
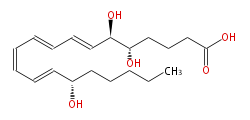
| (5S,6R,15S) -Trihydroxy- (trans-7,trans-9,cis-11,trans-13) -eicosatetraenoic acid | |
| |
| LXA4 | |
| Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Exact Mass | 352.224974134 |
| Average Mass | 352.46508 |
| SMILES | C(CCC(C=CC=CC=CC=CC(O)C(O)CCCC(O)=O)O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| diethyl ether, methanol. AdamsJet al. | |
| LXA4 is formed in vitro by a number of mechanisms from arachidonic acid, 15-HpETE, and leukotriene A4 (LTA4 ) Edenius_C et al. Serhan_CN et al.. Lipoxin A4 is produced by activated leukocytes Serhan_CN , Brady_HR et al.. | |
| Table0001 Adams_J et al. | |
| Dual lipoxygenation pathways are considered for lipoxin A4 synthesis from arachidonic acid; either 15-lipoxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase in leukocytes or 5-lipoxygenase in leukocytes and 12-lipoxygenase in platelets Serhan_CN . | |
| LXA is equipotent to LTB in inducing superoxide generation in human neutrophils (0.1 mu M) Serhan_CN et al.. LXA4 is associated with several other biological functions including leukocyte activation, chemotaxis promotion, natural killer cell inhibition, and monocyte migration and adhesion Serhan_CN et al. Ramstedt_U et al. Maddox_JF et al.. Lipoxin A4 is either vasoconstrictive or vasodilatory, and has immunoregulatory activities blocking the cytotoxic action of NK cell, inhibiting adherence and chemotaxis of leukocytes induced by FMLP, PAF or leukotriene B4 Serhan_CN . | |
| cDNA for a receptor specific for lipoxin A4 was cloned out of orphan cDNAs Fiore_S et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | TMS-derivs. ; 582(M+), 492, 482, 379, 289, 203, 173, 171. Serhan_CN et al. |
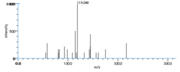
| UV Spectra | λ max: 302nm ε : 50,000, λ MeOHmax: 287,301 (ε 50,000) : 316nm AdamsJet al., Serhan_CN et al. |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | 1H-NMR(250MHz, 5% CD3OD/D2O ) : δ 0.8-0.9(brt, 3H), 1.2-1.8(m, 14H), 2.1-2.3(m, 2H), 3.4-3.6(m, 1H), 3.95-4.05(t, J=6.8Hz, 1H), 4.1-4.2(q, J=7.1Hz, 1H), 5.6-5.85(seven lines, 2H), 5.9-6.1(m, 2H), 6.2-6.45(m, 2H), 6.6-6.8(m, 2H). AdamsJet al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|