LBF20107PG01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=XPR1400 | |LipidBank=XPR1400 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA03010134 | |LipidMaps=LMFA03010134 | ||
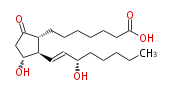
|SysName=7- [ | |SysName=7- [3R- Hydroxy- 2R- (3S-hydroxy-trans-1-octenyl) -5-oxocyclopentan-1R-yl] -heptanoic acid | ||
|Common Name=&&Prostaglandin E_1&&(8R,11R,12R,13E,15S) -11,15-Dihydroxy-9-oxo-13-prostenoic acid&&7- [3R- Hydroxy- 2R- (3S -hydroxy-1(E) -octenyl) -5-oxocyclopentan-1R-yl] -heptanoic acid&& | |||
|Melting Point=115-117°C | |Melting Point=115-117°C[[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Sjoevall_J:,Acta_Chem._Scand.,1960,14,1701|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Sjoevall_J:,Acta_Chem._Scand.,1960,14,1701}}]] | ||
| | |Optical=[ alpha ]_{578}=-61.6°(C=0.56, TETRAHYDROFURAN) [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535}}]] | ||
|Solubility=DIETHYL ETHER, ETHYL ACETATE , METHANOL [[Reference:Struijk_MCB:Beerthuis_RK:Pabon_HJJ:Van_Dorp_DA:,Recueil Travaux Quimiq Pays Bas,1966,85,1233|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Struijk_MCB:Beerthuis_RK:Pabon_HJJ:Van_Dorp_DA:,Recueil Travaux Quimiq Pays Bas,1966,85,1233}}]], TETRAHYDROFURAN [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535}}]] | |Solubility=DIETHYL ETHER, ETHYL ACETATE[[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Sjoevall_J:,Acta_Chem._Scand.,1960,14,1701|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Sjoevall_J:,Acta_Chem._Scand.,1960,14,1701}}]] , METHANOL [[Reference:Struijk_MCB:Beerthuis_RK:Pabon_HJJ:Van_Dorp_DA:,Recueil Travaux Quimiq Pays Bas,1966,85,1233|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Struijk_MCB:Beerthuis_RK:Pabon_HJJ:Van_Dorp_DA:,Recueil Travaux Quimiq Pays Bas,1966,85,1233}}]], TETRAHYDROFURAN [[Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535}}]] | ||
|Mass Spectra=METHYL ESTER ; m/e 350, 332, 319, 301, 279 [[Reference:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,J. Biol. Chem.,1966,241,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,J. Biol. Chem.,1966,241,257}}]] | |Mass Spectra=METHYL ESTER ; m/e 350, 332, 319, 301, 279 [[Reference:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,J. Biol. Chem.,1966,241,257|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hamberg_M:Samuelsson_B:,J. Biol. Chem.,1966,241,257}}]] | ||
|IR Spectra=METHYL ESTER ; | |IR Spectra=METHYL ESTER ; nu 1726, 1717sh, 1699, 980 cm^{-1} [[Reference:Hayashi_M:Miyamoto_T:,Metabolism and Disease (Taisha),1975,12,1461|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Miyamoto_T:,Metabolism and Disease (Taisha),1975,12,1461}}]] | ||
|NMR Spectra= | |NMR Spectra=^1 H-NMR(CDCl_3 +DMSO-d_6 ,TMS) : delta 5.70-5.51(m, 2H), 4.14-3.86(m, 2H), 2.72(d,d, 1H)[[Reference:Hayashi_M:Miyamoto_T:,Metabolism and Disease (Taisha),1975,12,1461|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Hayashi_M:Miyamoto_T:,Metabolism and Disease (Taisha),1975,12,1461}}]]. ^{13}C-NMR(CHCl_3 -CH_3 OH, TMS) : delta 215.2(C-9), 176.7(C-1), 136.6(C-14), 131.9(C-13), 72.9(C-15), 71.6(C-11), 54.6(C-8), 54.2(C-12), 45.9(C-10), 36.9(C-16), 33.8(C-2), 31.5(C-18), 29.0(C-4), 28.6(C-5), 27.4(C-7), 26.3(C-6), 25.0(C-17), 24.5(C-3), 22.5(C-19), 13.8(C-20) [[Reference:Lukacs_G:Piriou_F:Gero_SD:,Tetrah. Lett.,1973,,515|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Lukacs_G:Piriou_F:Gero_SD:,Tetrah. Lett.,1973,,515}}]] | ||
|Source=Prostaglandin E1 is contained in human seminal plasma in an amount of 25 microgram/ml [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382}}]], and has been found in ovine seminal plasma and seminal vesicle, human menstrual and amniotic flluid, human uterine endometrium, umbilical cord, placental vessels and decidua, frog spinal cord, rat adrenal, human and bovine thymus, frog intestine, rat fat tissue, and human phrenic nerve [[Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122}}]][[Reference:Speroff_L:Ramwell_PW:,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,1970,107,1111|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Speroff_L:Ramwell_PW:,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,1970,107,1111}}]][[Reference:Horton_EW:,Experientia,1965,21,113|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Experientia,1965,21,113}}]][[Reference:Karim_SM:Hillier_K:Devlin_J:,J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,1968,20,749|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Karim_SM:Hillier_K:Devlin_J:,J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,1968,20,749}}]][[Reference:Karim_SM:Sandler_M:Williams_ED:,Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother.,1967,31,340|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Karim_SM:Sandler_M:Williams_ED:,Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother.,1967,31,340}}]][[Reference:Kirtland_SJ:,Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids,1988,32,165|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Kirtland_SJ:,Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids,1988,32,165}}]]. | |Source=Prostaglandin E1 is contained in human seminal plasma in an amount of 25 microgram/ml [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:,Science,1967,157,382}}]], and has been found in ovine seminal plasma and seminal vesicle, human menstrual and amniotic flluid, human uterine endometrium, umbilical cord, placental vessels and decidua, frog spinal cord, rat adrenal, human and bovine thymus, frog intestine, rat fat tissue, and human phrenic nerve [[Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Physiol. Rev.,1969,49,122}}]][[Reference:Speroff_L:Ramwell_PW:,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,1970,107,1111|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Speroff_L:Ramwell_PW:,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,1970,107,1111}}]][[Reference:Horton_EW:,Experientia,1965,21,113|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horton_EW:,Experientia,1965,21,113}}]][[Reference:Karim_SM:Hillier_K:Devlin_J:,J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,1968,20,749|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Karim_SM:Hillier_K:Devlin_J:,J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,1968,20,749}}]][[Reference:Karim_SM:Sandler_M:Williams_ED:,Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother.,1967,31,340|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Karim_SM:Sandler_M:Williams_ED:,Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother.,1967,31,340}}]][[Reference:Kirtland_SJ:,Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids,1988,32,165|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Kirtland_SJ:,Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids,1988,32,165}}]]. | ||
|Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535}}]] {{Image200|LBF20107PG01FT0001.gif}} | |Chemical Synthesis=[[Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Corey_EJ:Vlattas_I:Harding_K:,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1969,91,535}}]] {{Image200|LBF20107PG01FT0001.gif}} | ||
|Metabolism=Prostagalndin E1 is produced from H1 at almost the same rate of E2 synthesis from H2 by an enzyme of bovine seminal vesicle [[Reference:Ogino_N:Miyamoto_T:Yamamoto_S:Hayaishi_O:,J. Biol. Chem.,1977,252,890|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Ogino_N:Miyamoto_T:Yamamoto_S:Hayaishi_O:,J. Biol. Chem.,1977,252,890}}]]. | |Metabolism=Prostagalndin E1 is produced from H1 at almost the same rate of E2 synthesis from H2 by an enzyme of bovine seminal vesicle [[Reference:Ogino_N:Miyamoto_T:Yamamoto_S:Hayaishi_O:,J. Biol. Chem.,1977,252,890|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Ogino_N:Miyamoto_T:Yamamoto_S:Hayaishi_O:,J. Biol. Chem.,1977,252,890}}]]. | ||
|Symbol=PGE1 | |||
|Biological Activity=Prostaglandin E1 is generally considered as active as E2, and the biological activities of both compounds are compared in references [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]][[Reference: Horton_EW:Main_IHM:,Mem._Soc._Endocr.,1966,14,29|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference: Horton_EW:Main_IHM:,Mem._Soc._Endocr.,1966,14,29}}]]. However, platelet aggregation is inhibited by prostaglandin E1 whereas prostaglandin E2 is much less active [[Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Bergstrom_S:Carlson_LA:Weeks_JR:,Pharmacol. Rev.,1968,20,1}}]]. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:59, 21 October 2010
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | XPR1400 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA03010134 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20107PG01 |
| Prostaglandin E1 | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
| 7- [3R- Hydroxy- 2R- (3S-hydroxy-trans-1-octenyl) -5-oxocyclopentan-1R-yl] -heptanoic acid | |
| |
| PGE1 | |
| Formula | C20H34O5 |
| Exact Mass | 354.240624198 |
| Average Mass | 354.48096000000004 |
| SMILES | C(CC[C@@H](O)C=C[C@H]([C@H]1CCCCCCC(O)=O)[C@@H](CC1=O)O)CC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| 115-117°C Bergstrom_S et al. | |
| [ α ]578=-61.6°(C=0.56, TETRAHYDROFURAN) Corey_EJ et al. | |
| DIETHYL ETHER, ETHYL ACETATE BergstromSet al. , METHANOL Struijk_MCB et al., TETRAHYDROFURAN Corey_EJ et al. | |
| Prostaglandin E1 is contained in human seminal plasma in an amount of 25 microgram/ml Bergstrom_S , and has been found in ovine seminal plasma and seminal vesicle, human menstrual and amniotic flluid, human uterine endometrium, umbilical cord, placental vessels and decidua, frog spinal cord, rat adrenal, human and bovine thymus, frog intestine, rat fat tissue, and human phrenic nerve Horton_EW Speroff_L et al. Horton_EW Karim_SM et al. Karim_SM et al. Kirtland_SJ . | |
Corey_EJ et al.  | |
| Prostagalndin E1 is produced from H1 at almost the same rate of E2 synthesis from H2 by an enzyme of bovine seminal vesicle Ogino_N et al.. | |
| Prostaglandin E1 is generally considered as active as E2, and the biological activities of both compounds are compared in references Bergstrom_S et al. Horton_EW et al.. However, platelet aggregation is inhibited by prostaglandin E1 whereas prostaglandin E2 is much less active Bergstrom_S et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | METHYL ESTER ; m/e 350, 332, 319, 301, 279 HambergMet al. |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | METHYL ESTER ; ν 1726, 1717sh, 1699, 980 cm-1 HayashiMet al. |
| NMR Spectra | 1H-NMR(CDCl3+DMSO-d6,TMS) : δ 5.70-5.51(m, 2H), 4.14-3.86(m, 2H), 2.72(d,d, 1H) HayashiMet al.. 13C-NMR(CHCl3-CH3OH, TMS) : δ 215.2(C-9), 176.7(C-1), 136.6(C-14), 131.9(C-13), 72.9(C-15), 71.6(C-11), 54.6(C-8), 54.2(C-12), 45.9(C-10), 36.9(C-16), 33.8(C-2), 31.5(C-18), 29.0(C-4), 28.6(C-5), 27.4(C-7), 26.3(C-6), 25.0(C-17), 24.5(C-3), 22.5(C-19), 13.8(C-20) LukacsGet al. |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|