LBF20406SC01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|LipidBank=DFA0213 | |LipidBank=DFA0213 | ||
|LipidMaps=LMFA01030001 | |LipidMaps=LMFA01030001 | ||
|SysName=5, 8, 11, 14-Eicosatetraenoic | |SysName=(cis-5,cis-8,cis-11,cis-14) -Eicosatetraenoic acid | ||
|Common Name=&&Arachidonic acid&& | |Common Name=&&Arachidonic acid&&(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z) -Eicosatetraenoic acid&& | ||
|Melting Point=-49.5 °C | |Melting Point=-49.5 °C | ||
|Boiling Point=163 °C at 1 mmHg | |Boiling Point=163 °C at 1 mmHg | ||
|Density=0.9082 at 20 °C | |Density=0.9082 at 20 °C | ||
|Refractive=1.4824 at 20 °C | |Refractive=1.4824 at 20 °C | ||
|Solubility=soluble in acetone, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether. | |Solubility=soluble in acetone, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether.<!--0224--><!--0225--><!--0328--><!--0347--> | ||
|Source=Constituent of many animal phospholipids, also of some ferns and mosses. Confinded to fats of land animals; brain, liver, glandular and egg lipids. | |Source=Constituent of many animal phospholipids, also of some ferns and mosses. Confinded to fats of land animals; brain, liver, glandular and egg lipids. | ||
|Chemical Synthesis= | |Chemical Synthesis= | ||
|Metabolism=Metabolic product of linoleic acid (9,12-18:2). The synthesis of 5,8,11,14-20:4 occurs via the following reaction sequence in the endoplasmic reticulum [[Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471}}]]: 9,12-18:2 --> 6,9,12-18:3 --> 8,11,14-20:3 --> 5,8,11,14-20:4. | |Metabolism=Metabolic product of linoleic acid (9,12-18:2). The synthesis of 5,8,11,14-20:4 occurs via the following reaction sequence in the endoplasmic reticulum [[Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Sprecher_H:Luthria_DL:Mohammed_BS:Baykousheva_SP:,J. Lipid. Res.,1995,36,2471}}]]: 9,12-18:2 --> 6,9,12-18:3 --> 8,11,14-20:3 --> 5,8,11,14-20:4. | ||
|Symbol=AA / Ara / C20:4n-6 / C20:4 | |Symbol=AA / Ara / C20:4n-6 / C20:4 omega 6 | ||
|Biological Activity=There are two groups of essential fatty acids, the n-6 (or | |Biological Activity=There are two groups of essential fatty acids, the n-6 (or omega 6) and the n-3 (or omega 3). Arachidonic acid is n-6 fatty acids. Essential fatty acid deficiency causes skin lesion and growth retardation. Dietary supplementation of either linoleate, gamma -linoleate or arachidonate prevents such symptoms completely. The n-6 essential fatty acids have at least four roles [[Reference:Horrobin_DF:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1992,31,163|{{RelationTable/GetFirstAuthor|Reference:Horrobin_DF:,Prog. Lipid Res.,1992,31,163}}]]: 1) Modulation of membrane structure. 2) Formation of bioactive molecules called eicosanoids. Arachidonic acid, which is nomally found esterifing sn-2 position of phospholipids, is released by the action of phospholipase A_2 . Free arachidonate is used for precursors of eicosanoids, such as PG_2 series of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes. 3) Control of the water impermeability of the skin. 4) Regulation of cholesterol synthesis and transport. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Lipid/Footer}} | {{Lipid/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:27, 20 July 2016
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0213 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030001 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF20406SC01 |
| Arachidonic acid | |
|---|---|
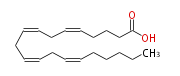
| |
| Structural Information | |
| (cis-5,cis-8,cis-11,cis-14) -Eicosatetraenoic acid | |
| |
| AA / Ara / C20:4n-6 / C20:4 omega 6 | |
| Formula | C20H32O2 |
| Exact Mass | 304.240230268 |
| Average Mass | 304.46688 |
| SMILES | C(CC=CCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCC(O)=O)CCC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| -49.5 °C | |
| 163 °C at 1 mmHg | |
| 0.9082 at 20 °C | |
| 1.4824 at 20 °C | |
| soluble in acetone, methyl alcohol, ether and petroleum ether. | |
| Constituent of many animal phospholipids, also of some ferns and mosses. Confinded to fats of land animals; brain, liver, glandular and egg lipids. | |
| Metabolic product of linoleic acid (9,12-18:2). The synthesis of 5,8,11,14-20:4 occurs via the following reaction sequence in the endoplasmic reticulum Sprecher_H et al.: 9,12-18:2 --> 6,9,12-18:3 --> 8,11,14-20:3 --> 5,8,11,14-20:4. | |
| There are two groups of essential fatty acids, the n-6 (or omega 6) and the n-3 (or omega 3). Arachidonic acid is n-6 fatty acids. Essential fatty acid deficiency causes skin lesion and growth retardation. Dietary supplementation of either linoleate, gamma -linoleate or arachidonate prevents such symptoms completely. The n-6 essential fatty acids have at least four roles Horrobin_DF : 1) Modulation of membrane structure. 2) Formation of bioactive molecules called eicosanoids. Arachidonic acid, which is nomally found esterifing sn-2 position of phospholipids, is released by the action of phospholipase A_2 . Free arachidonate is used for precursors of eicosanoids, such as PG_2 series of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes. 3) Control of the water impermeability of the skin. 4) Regulation of cholesterol synthesis and transport. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|