LBF18303SC01: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|Density=dX<sub>4</sub><sup>20</sup> 0.9164 | |Density=dX<sub>4</sub><sup>20</sup> 0.9164 | ||
|Refractive=1.4678 at 50°C | |Refractive=1.4678 at 50°C | ||
|Solubility=soluble in acetone, ethanol, ether and petroleum ether. | |Solubility=soluble in acetone, ethanol, ether and petroleum ether.<!--0400--> | ||
|Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF18303SC01CH0001.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | |Chromatograms=Gas liquid chromatogram {{Image200|LBF18303SC01CH0001.gif}} (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). | ||
|Source=Linseed, perilla, and hemp oils; drying oils. | |Source=Linseed, perilla, and hemp oils; drying oils. | ||
Revision as of 01:30, 27 January 2010
| LipidBank Top (トップ) |
Fatty acid (脂肪酸) |
Glycerolipid (グリセロ脂質) |
Sphingolipid (スフィンゴ脂質) |
Journals (雑誌一覧) |
How to edit (ページの書き方) |
| IDs and Links | |
|---|---|
| LipidBank | DFA0191 |
| LipidMaps | LMFA01030152 |
| CAS | |
| KEGG | {{{KEGG}}} |
| KNApSAcK | {{{KNApSAcK}}} |
| mol | LBF18303SC01 |
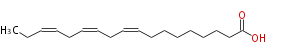
| α-Linolenic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Structural Information | |
| cis-9, cis-12, cis-15-Octadecatrienoic acid | |
| |
| aLnA / C18:3n-3 / C18:3w3 / aLnn | |
| Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Exact Mass | 278.224580204 |
| Average Mass | 278.4296 |
| SMILES | CCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Physicochemical Information | |
| -11.3 to -11°C | |
| 125°C at 0.05 mmHg | |
| dX420 0.9164 | |
| 1.4678 at 50°C | |
| soluble in acetone, ethanol, ether and petroleum ether. | |
| Linseed, perilla, and hemp oils; drying oils. | |
| Linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is synthesized from oleic acid (18:1n-9) by desaturation of D12-desaturase, and a-linolenic acid (18:3n-3) is formed from linoleic acid by desaturation reaction of D15-desaturase. Since both D12- and 15-desaturases are present in plant cells, a-linolenic acid is synthesized in plants, and relatively enriched in leaves (photosynthetic tissues). On the other hand, these desaturases are not present in animal cells, neither linoleic nor a-linolenic acid is biosynthesized in animal cells in vivo. When ingested by animals, a-linolenic acid is desaturated, elongated and chain-shortened to form eicosapantaenoic acid (20:5n-3, EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3, DHA) Voss_A et al. Moore_SA et al.. No interconversion between the n-6 and n-3 series in mammals., Nutritionally, it is important to note that different foods contain different proportions of n-6/n-3 and therefore the n-6/n-3 ratio in tissue lipids change significantly depending on the choice of foods. Although plants synthesize and store linoleic acid and a-linolenic acid as well as saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids in grains, the proportions of these fatty acids in different vegetable oils differ greatly. Safflower and sunflower oil contain high levels of linoleate, while perilla and linseed oil are rich in a-linolenic acid. | |
| Dietary a-linolenic acid can be further elongated and desaturated to form the long-chain n-3 fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DHA), which are uniquely rich in neural membranes of retina and brain in mammals. It has been reported that n-3 fatty acid deficiency produces reduced learning ability Yamamoto_N et al., impaired vision, abnormal electroretinogram Neuringer_M et al. Neuringer_M et al. and polydipsia Reisbick_S et al.. Dietary fat manipulation of perilla oil rich in a-linolenic acid reduces colonic damage in experimental Crohn's disease Shoda_R et al. Shoda_R et al.. | |
| Spectral Information | |
| Mass Spectra | |
| UV Spectra | |
| IR Spectra | |
| NMR Spectra | |
| Other Spectra | |
| Chromatograms | Gas liquid chromatogram  (provided by Dr. Akiko Horiuchi). |
| Reported Metabolites, References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|