Category:LBSG: Difference between revisions
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
Sialic acid is a collective noun and comprises a family of derivatives of neuraminic acid (5-amino- 3,5-dideoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid)<ref>Roland Schauer "Sialic Acids - Chemistry, Metabolism and Function" Springer-Verlag, 1982.</ref>. | Sialic acid is a collective noun and comprises a family of derivatives of neuraminic acid (5-amino- 3,5-dideoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid)<ref>Roland Schauer "Sialic Acids - Chemistry, Metabolism and Function" Springer-Verlag, 1982.</ref>. | ||
Nowadays, there are over 30 derivatives of neuraminic acid, including N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuAc), N-glycolyl neuraminic acid (NeuGc), deamino neuraminic acid (KDN: 3-deoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid) | Nowadays, there are over 30 derivatives of neuraminic acid, including: | ||
* N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuAc), | |||
* N-glycolyl neuraminic acid (NeuGc), and | |||
* deamino neuraminic acid (KDN: 3-deoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid). | |||
| | | | ||
シアル酸は、ノイラミン酸(5-アミノ-3,5-ジデオキシ-D-グリセロ-D-ガラクト-ノヌロン酸)に由来する物質の総称です。 | シアル酸は、ノイラミン酸(5-アミノ-3,5-ジデオキシ-D-グリセロ-D-ガラクト-ノヌロン酸)に由来する物質の総称です。 | ||
現在、ノイラミン酸には以下を含む30 種以上の誘導体が知られています。 | |||
* N-アセチルノイラミン酸 (NeuAc) | |||
* N-グリコリルノイラミン酸 (NeuGc) | |||
* デアミノノイラミン酸 (KDN: 3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nonulosonic acid) | |||
}} | }} | ||
===History=== | ===History=== | ||
Revision as of 09:51, 12 February 2016
Sialic acid
Sialic acid is a collective noun and comprises a family of derivatives of neuraminic acid (5-amino- 3,5-dideoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid)[1]. Nowadays, there are over 30 derivatives of neuraminic acid, including:
|
シアル酸は、ノイラミン酸(5-アミノ-3,5-ジデオキシ-D-グリセロ-D-ガラクト-ノヌロン酸)に由来する物質の総称です。 現在、ノイラミン酸には以下を含む30 種以上の誘導体が知られています。
|
History
|
|
- ↑ Roland Schauer "Sialic Acids - Chemistry, Metabolism and Function" Springer-Verlag, 1982.
- ↑ A Lundblad "Gunnar Blix and his discovery of sialic acids. Fascinating molecules in glycobiology" Ups J Med Sci. 120(2):104–112, 2015
- ↑ JN Kanfer and S Hakomori "Sphingolipid biochemistry" Chapter 1, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012
Ganglioside
Ganglioside is a glycosphingolipid with one or more sialic acid. Major structures include ganglio, lacto, and neolacto series. In mammalian brains, ganglioside contains primarily d20:1 long chain base and stearic acid (18:0, about 80%) and does not include hydroxy fatty acids. |
酸性糖であるシアル酸を含む糖脂質をガングリオシドと呼び、主要系列にガングリオ、ラクト、ネオラクト等を含みます。哺乳類の脳では基本的にd20:1の長鎖塩基とステアリン酸(18:0)で構成され、酸化脂質は含みません。 |
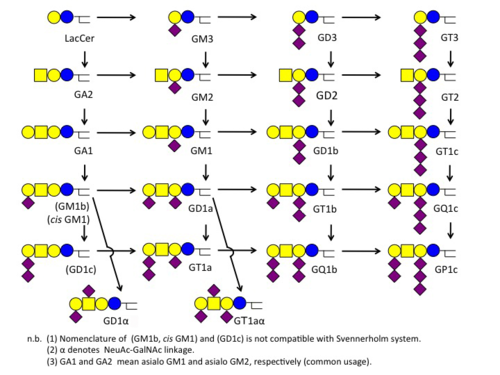
Svennerholm Notation
スヴェナーホルム表記
The notation was proposed by the Swedish scientist, Lars Svennerholm. Each alpha-numeric digit stands for the number of sialic acids or sugars. |
スウェーデンの科学者 Lars Svennerholm が導入した記法です。各桁の数字やアルファベットはシアル酸の数や糖の数を意味します。 |
| Indicated number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of sialic acids | GM | GD | GT | GQ |
| Number of sugars | tetraose (4) | triose (3) | lactose (2) | galactose (1) |
| Sialic acids attached to the second Gal | a | b | c | - |
- Examples
- GQ1b ... 4 sialic acids (GQ), 4 sugars (GQ1), 2 sialic acids attached to the 2nd galactose (GQ1b)
- GM2 ... 1 sialic acids (GM), 3 sugars (GM2).
Sulfatide
|
硫酸化糖脂質の中でもガラクトースの3位の水酸基に硫酸を導入したものをスルファチドと呼び、ガラクトシルセラミドと並んでミエリンの主要糖脂質です。 |
This category currently contains no pages or media.