Category:LBSG
Sialic acid
Sialic acid is a collective noun and comprises a family of derivatives of neuraminic acid (5-amino- 3,5-dideoxy- D-glycero- D-galacto- nonulosonic acid)[1]. Nowadays, there are over 30 derivatives of neuraminic acid, including:
|
シアル酸は、ノイラミン酸(5-アミノ-3,5-ジデオキシ-D-グリセロ-D-ガラクト-ノヌロン酸)に由来する物質の総称です。 現在、ノイラミン酸には以下を含む30 種以上の誘導体が知られています。
|
【ここに構造を入れること】
History
|
|
- ↑ Schauer R "Sialic Acids - Chemistry, Metabolism and Function" Springer-Verlag, 1982.ISBN 978-3-7091-8680-0
- ↑ Lundblad A "Gunnar Blix and his discovery of sialic acids. Fascinating molecules in glycobiology" Ups J Med Sci. 2015; 120:104–112 PMID 25921326
- ↑ Gottschalk A. "Structural Relationship between Sialic Acid, Neuraminic Acid and 2-Carboxy-Pyrrole" Nature 1955; 176, 881 - 882 doi:10.1038/176881a0
- ↑ JKanfer JN and Hakomori S "Sphingolipid biochemistry (Handbook of Lipid Research 3)" Chapter 1, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012 ISBN-13: 978-1475703986
Ganglioside
Ganglioside is a glycosphingolipid with one or more sialic acid. It was named by Klenk E. in 1942 as the major sphingolipid in ganglion, a nerve cell cluster.[1] In vertebrate, close to 190 gangliosides have been identified.[2] They reside on lipid rafts of cell membranes, and involve in many cellular functions. Major structures with sialic acids include ganglio, lacto, and neolacto series. |
酸性糖であるシアル酸を含む糖脂質をガングリオシドと呼びます。神経細胞の集まりである神経核 (ganglion) に多いことから Klenk E.により1942年に命名されました。 脊椎動物では現在およそ190種のガングリオシドが見出されています。ガングリオシドは細胞膜の脂質ラフトに存在し、多くの生理機能に関わっています。シアル酸の結合する主要系列はガングリオ、ラクト、ネオラクト等です。 |
- ↑ Sweeley CC, Siddiqui B. "Chemistry of Mammalian Glycolipids" Chapter 6 in The Glycoconjugates Volume I: Mammalian Glycoproteins and Glycolipids (Ed. Horowitz MI, Pigman W) 1977 Elsevier Inc. ISBN: 978-0-12-356101-5
- ↑ Yu RK, Tsai YT, Ariga T, Yanagisawa M. (2011) Structures, biosynthesis, and functions of gangliosides--an overview" J Oleo Sci. 60(10):537-44. PMID 21937853
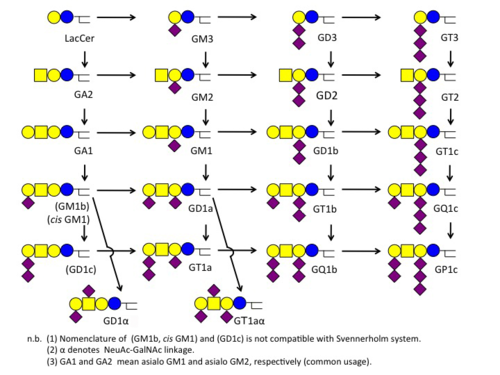
Svennerholm Notation
スヴェンネルホルム表記
The notation was proposed by the Swedish scientist, Lars Svennerholm. Each alpha-numeric digit stands for the number of sialic acids or sugars. |
スウェーデンの科学者 Lars Svennerholm が導入した記法です。各桁の数字やアルファベットはシアル酸の数や糖の数を意味します。 |
【この表は再構成する】
| Abbreviation | GM | GD | GT | GQ | GP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suffix Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Core | Gg4Cer | Gg3Cer | LacCer | GalCer | |
| Number of sialic acids (attached to IIGal) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Suffix Alphabet (only for Gg4Cer) | a | b | c |
- Examples
- GQ1b ... 4 sialic acids (GQ), 4 sugars (GQ1), 2 sialic acids attached to the 2nd galactose (GQ1b)
- GM2 ... 1 sialic acids (GM), 3 sugars (GM2).
Sulfatide
|
硫酸化糖脂質の中でもガラクトースの3位の水酸基に硫酸を導入したものをスルファチドと呼び、ガラクトシルセラミドと並んでミエリンの主要糖脂質です。 硫酸化糖脂質には硫酸化される糖鎖の違いにより十数種類が同定されています。その中でもガラクトシルセラミドのガラクトースの3位に水酸基に硫酸を導入したものをガラクトシルスルファチドと呼びます。ラット腎臓にはグルコシルセラミドに硫酸基が結合したグルコシルスルファチドも報告があります。スルファチドは神経系、腎臓、呼吸器、消化器などさまざまな組織に存在する糖脂質で、ミエリン形成に関わるほか、糖尿病、免疫系、血栓形成、細菌感染、ウィルス感染など生理作用は多岐にわたります。リソソーム病である異染性白質ジストロフィー(metachromatic leukodystrophy)という先天性代謝異常症は、スルファチド分解酵素(ASA)あるいは活性化因子の欠損か低下により起こります。 |
- ↑ Takahashi T. and Suzuki T. Role of sulfatide in normal and pathological cells and tissues.J Lipid Res. 2012 53: 1437–1450. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R026682
- ↑ Takahashi T, Suzuki T. Role of sulfatide in influenza A virus replication. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015 38:809-16. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00119.
- ↑ Honke K. Biosynthesis and biological function of sulfoglycolipids. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2013 89:129-38. doi: 10.2183/pjab.89.129
This category currently contains no pages or media.