Category:LBS: Difference between revisions
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
=={{Bilingual|構造コード|Structure Code}}== | |||
<table><tr align="top"> | <table><tr align="top"> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
===First Code for Glycosphingolipid=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" align="right" | {| class="wikitable" align="right" | ||
! First sugar || Code || Sequence || Common Name | ! First sugar || Code || Sequence || Common Name | ||
| Line 185: | Line 185: | ||
| | | | ||
{| style="background:#f9f9f9" cellspacing=0 cellpadding=0 | {| style="background:#f9f9f9" cellspacing=0 cellpadding=0 | ||
|GalNAc<sub>β1 | |GalNAc<sub>β1-4</sub> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|GlcNAc<sub>β1 | |GlcNAc<sub>β1</sub>/<sup>3</sup> | ||
|} | |} | ||
|Gal<sub>β1−4</sub> Glc<sub>β1−1</sub> Cer</td></tr> | |Gal<sub>β1−4</sub> Glc<sub>β1−1</sub> Cer</td></tr> | ||
| Line 222: | Line 222: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td valign="top"> | <td valign="top"> | ||
===First Code for Glycosphingolipid=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! First sugar || Code || Common Name || Sequence | ! First sugar || Code || Common Name || Sequence | ||
| Line 250: | Line 250: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr></table> | </tr></table> | ||
===Second Code for subsequent sugars=== | ===Second Code for subsequent sugars=== | ||
Revision as of 21:29, 20 November 2014
Sphingolipid
Upper classes: LB
Class Overview
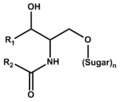
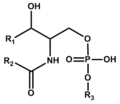
The Sphingolipid category (LBS) in the database includes glycosphingolipid and phosphosphingolipid.
| Sphingolipid Overview | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Glyco-sphingolipid (including its lyso form) |
Phospho-sphingolipid (including glycosyl phosphoinositolceramide or GIPC) | |
Sphingosine & Ceramide
Sphingolipids were first isolated from brain by J.L.W. Thudichum (1829-1901) as lipids of unknown function and structure. The name "sphingo" comes from the Greek word sphingein for holding tight. (The Sphinx also comes from this word root. See the Wikipedia article in English., as well as sphincter muscle.) The basic structure is a long-chain base, usually sphingosine (2-amino-4-octadecene-1,3-diol), whose amino-group is acylated with a long-chain fatty acid. This hydrophobic structure is called ceramides. |
スフィンゴ脂質は J.L.W. Thudichum (1829-1901) により機能や構造未知の脂質として脳から見いだされました。スフィンゴという名前はギリシャ語の sphingein に由来しており、「固く縛る」という意味です。(スフィンクスの語源も之に同じで、括約筋のことを英語で sphincter muscle といいます。)基本骨格は長鎖塩基 (長鎖アミノアルコール、通常はスフィンゴシン) のアミノ基が長鎖脂肪酸とアミド結合したもので、セラミドと呼ばれます。 |
Ceramides with the sphingosine base are prevalent as membrane components of eukaryotic cells. Those with the phytosphingosine base localize in particular organs such as small intestines. Sphingomyelin is a ceramide with phosphocholine. |
スフィンゴシンをもつセラミドは細胞組織の膜成分として普遍的に存在します。その他にも臓器特異的にフィトスフィンゴシンを含むセラミドが知られています。セラミドにホスフォコリンがついたものが有名なスフィンゴミエリンです。 |
Biosynthesis
Sphingosine is synthesized from decarboxylating condensation of palmitoyl CoA with serine. It is a 18-carbon amino alcohol (16 carbons from palmitic acid and 2 from serine) with one unsaturated bond. |
スフィンゴシンはパルミトイルCoAがアミノ酸セリンと脱炭酸縮合して生成します。炭素を18個含むアミノアルコール(16個がパルミチン酸、2個がセリン由来)で不飽和結合を1つ含んでいます (2-amino-4-octadecene-1,3-diol)。 |
Sphingolipid スフィンゴ脂質
Common Abbreviations
Page/ID Classification
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Structure Code
First Code for Glycosphingolipid
|
First Code for Glycosphingolipid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Second Code for subsequent sugars
|
|
|